iostat – Report Central Processing Unit (CPU) statistics and input/output statistics for devices and partitions.
The iostat command is used for monitoring system input/output device loading by observing the time the devices are active in relation to their average transfer rates. The iostat command generates reports that can be used to change system configuration to better balance the input/output load between physical disks.
The first report generated by the iostat command provides statistics concerning the time since the system was booted. Each subsequent report covers the time since the previous report. All statistics are reported each time the iostat command is run. The report consists of a CPU header row followed by a row of CPU statistics. On multiprocessor systems, CPU statistics are calculated system-wide as averages among all processors. A device header row is displayed followed by a line of statistics for each device that is configured.
The interval parameter specifies the amount of time in seconds between each report. The first report contains statistics for the time since system startup (boot). Each subsequent report contains statistics collected during the interval since the previous report. The count parameter can be specified in conjunction with the interval parameter. If the count parameter is specified, the value of count determines the number of reports generated at interval seconds apart. If the interval parameter is specified without the count parameter, the iostat command generates reports continuously.
iostat is part of sysstat package. To install on Debian/Ubuntu, run
apt install sysstat
To enable sysstat to collect data, edit file
vi /etc/default/sysstat
Find
ENABLED="false"
Replace with
ENABLED="true"
To see current IO Usage, run
iostat
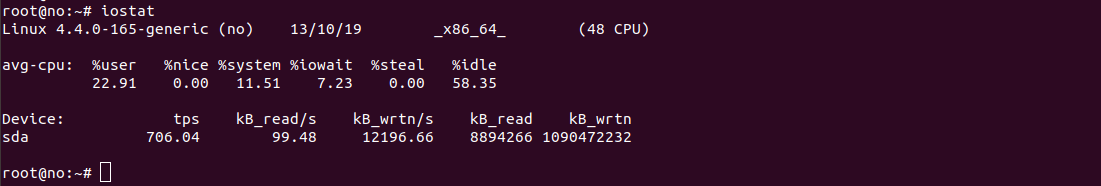
To show information in one line, run
iostat -xkd 2 5
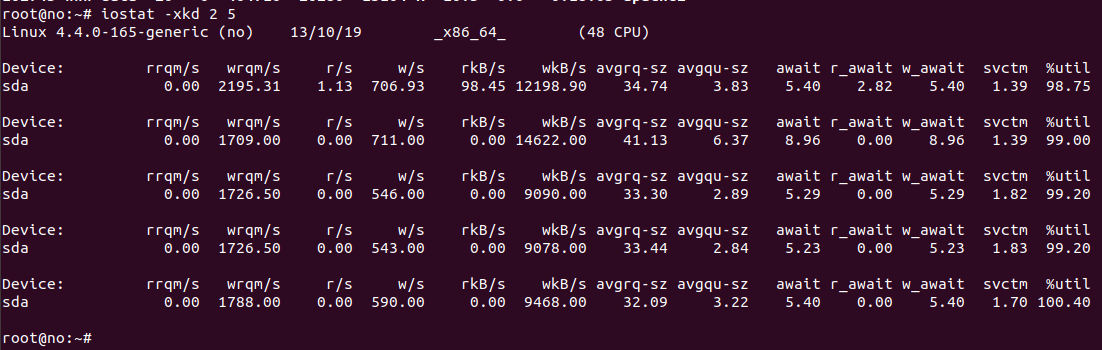
The number 2 is to print stats every 2 seconds. 5 is to print the stats 5 times.
Other iostat options
iostat -x iostat -x 2 5
Related Posts

Leave a Reply