systemd-timesyncd is a system service in Linux operating systems that provides time synchronisation with NTP servers. It continuously adjusts the system clock to ensure accurate timekeeping, which is crucial for various system operations, time-sensitive applications, and network synchronisation.
To configure systemd-timesyncd, edit file
vi /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf
Add following
[Time] NTP= FallbackNTP=time.google.com
Leaving NTP= uncommented and assigned to an empty string resets the list of NTP servers, including any per-interface assignments. This prevents inadvertently moving between smeared and un-smeared time servers. Configuring Google Public NTP as the fallback server will cause it to be selected as the only NTP server.
If you want to use debian maintained NTP servers, use
[Time] NTP= FallbackNTP=0.debian.pool.ntp.org 1.debian.pool.ntp.org 2.debian.pool.ntp.org 3.debian.pool.ntp.org
Restart systemd-timesyncd
systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd.service
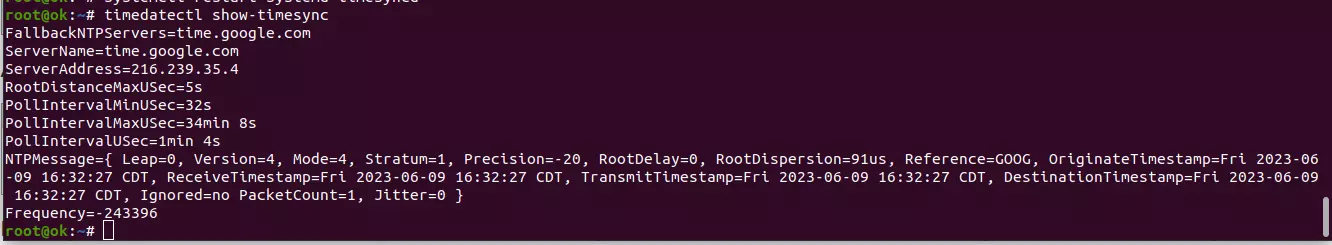
You can verify NTP server with command
timedatectl show-timesync | grep ServerName
Back to time

