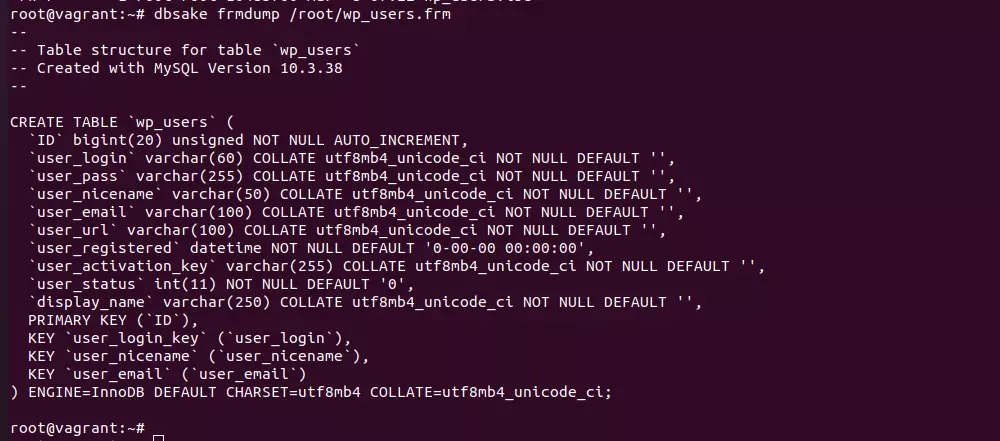
Since MySQL 5.5, InnoDB is the default storage engine due to its reliability, performance, and feature set. Switching from MyISAM to InnoDB is strongly recommended for most modern MySQL applications.
InnoDB is a transactional storage engine, meaning it fully supports ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties. You can safely roll back transactions in case of an error, preserving data integrity. MyISAM is non-transactional; it cannot roll back incomplete operations, which can lead to data corruption and inconsistencies in the event of a crash or error.
InnoDB uses row-level locking. This lets multiple users update different rows simultaneously without locking the entire table, so it excels in write-heavy and highly concurrent environments—like e-commerce platforms or busy web apps. MyISAM, by contrast, uses table-level locking, meaning any write operation locks the whole table, making it much less efficient for concurrent reads and writes.
InnoDB comes with robust automatic crash recovery. Its transactional logs allow it to recover data automatically in case of a server crash or power failure. MyISAM has only basic recovery options and is much more prone to corruption after unexpected shutdowns.
To list all MyISAM databases on your MySQL server, run
SELECT
table_schema AS database_name,
table_name
FROM
information_schema.tables
WHERE
engine = 'MyISAM'
AND table_schema NOT IN ('information_schema', 'sys', 'performance_schema', 'mysql');To list all MyISAM tables in a specific database, run
SELECT
table_name
FROM
information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_schema = 'your_database_name'
AND engine = 'MyISAM';To convert a table into InnoDB engine, use:
ALTER TABLE your_table_name ENGINE=InnoDB;Back to MySQL