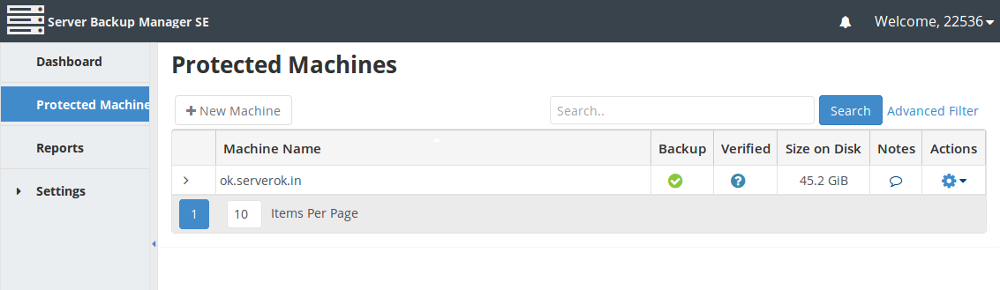
To restore backup, login to R1Soft Server Backup Manager. Go to Protected Machines. This page will list all available servers.
Click on wheel icon on right side.
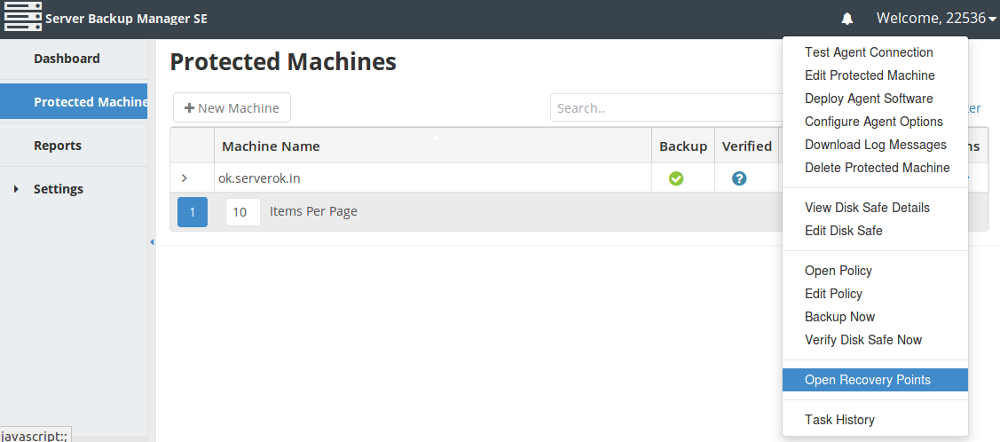
Click “Open Recovery Points” in the pop up menu. You get a new window with all available recovery points.
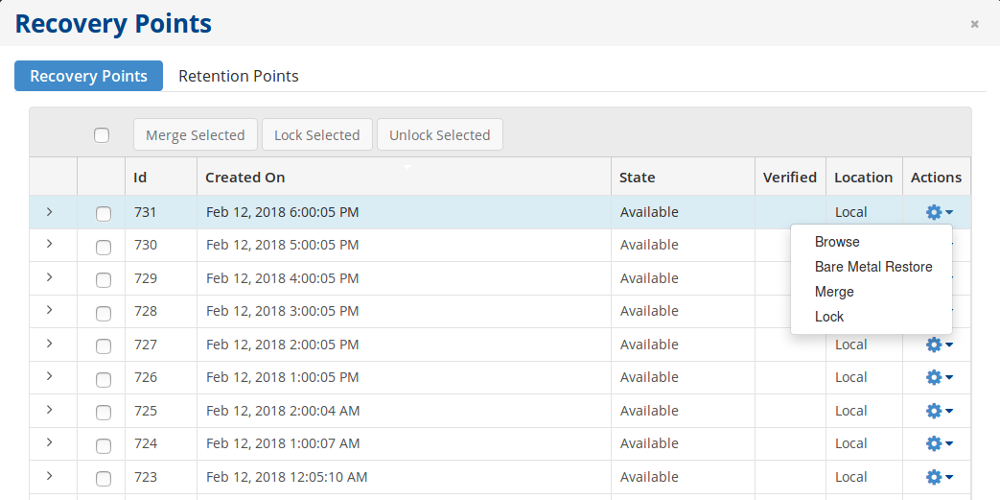
Click on the wheel icon.
In the popup menu, you will see “Browse” and “Bare Metal Restore”.
Bare Metal Restore
This is useful when you need to restore a server as is. Everything get restored exactly like in your old server. But only possible if you have physical access to server.
Download backup files
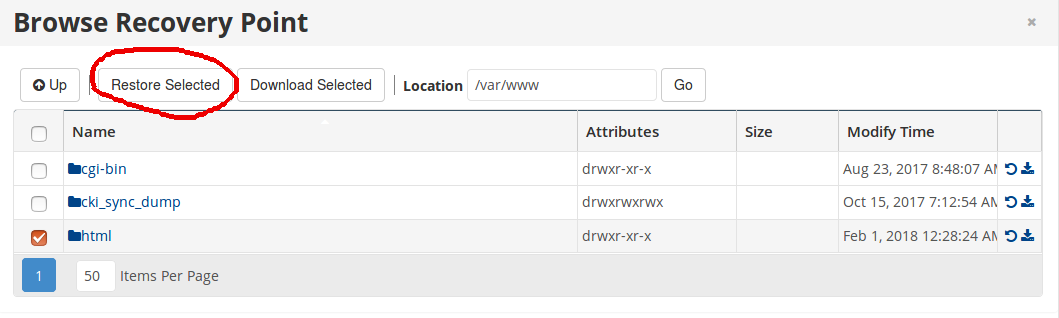
Browse option allow you to browse files and restore files and folders.
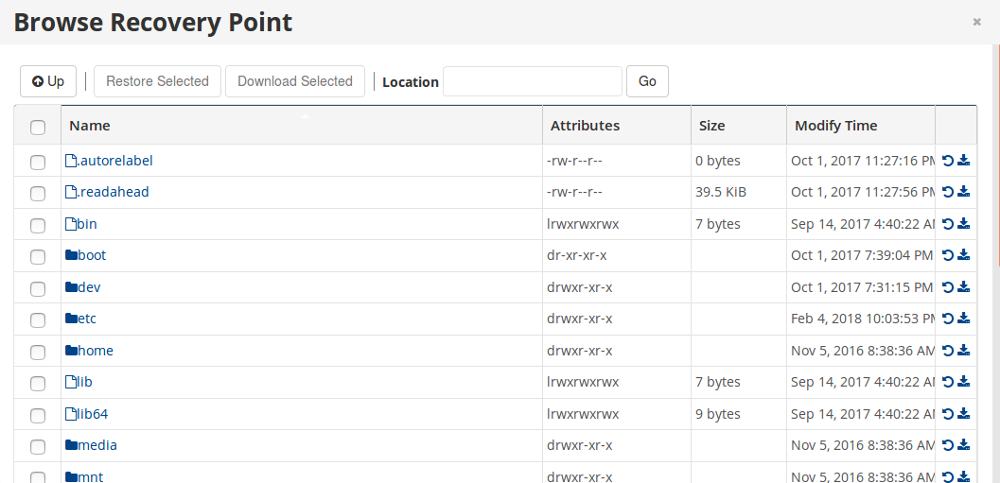
You can go inside a folder by double clicking the folder name. To download a folder or file as compressed file, click the download icon on right side.
Restore on same server
You can restore a file on same server. This will replace existing files on the server with files from backup. Always take a copy of the files before you do this.