Symlink attack exploits the way Linux operating systems handle symbolic links (symlinks). A symlink is a pointer to another file or directory that is used by the operating system to access the linked file or directory. In a symlink attack, an attacker creates a symbolic link that points to a file or directory that the attacker does not have permission to access. When the web server attempts to access the linked file or directory, the attacker can gain access to it.
Symlink attacks can be used to gain access to sensitive data. On a Cpanel Server, hackers usually create a symlink to common configuration files used by popular CMS on other hosting accounts on the same server. With this hackers can get database credentials of other websites hosted on the server. Many CMS store user credentials in the MySQL database, and they will be able to change passwords and gain access to websites.
Solution 1: CloudLinux CageFS (Paid)
The best way to prevent a symlink attack on the Cpanel server is to use CloudLinux CageFS, this isolates each site into its own isolated areas, so one website’s files won’t be able to another site.
Solution 2: mod_ruid2
If you are not using CloudLinux, you can use the following method to protect against the symlink attack. mod_ruid2 is an Apache module, that can be enabled in EasyApache 4.
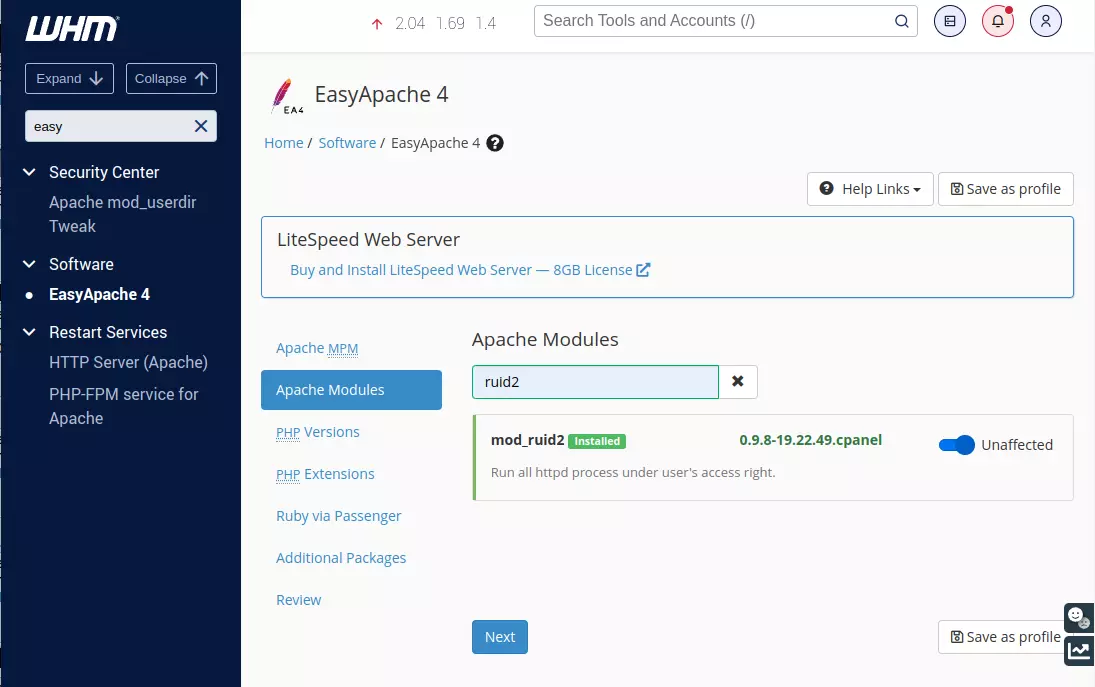
In WHM > Software > EasyApache 4, enable mod_ruid2.
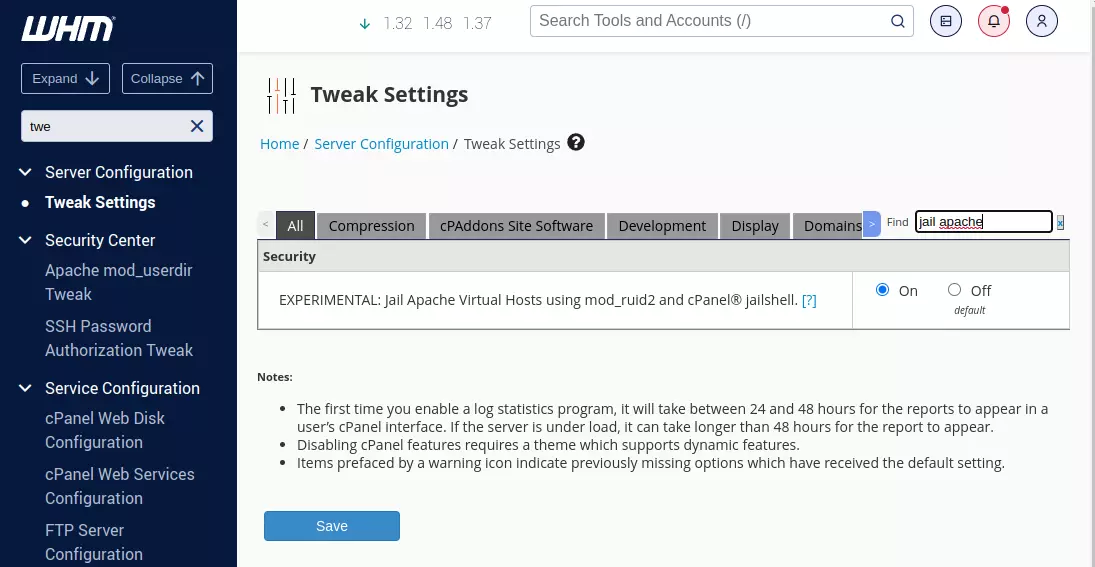
Under WHM > Server Configuration > Tweak Settings, enable jail Apache
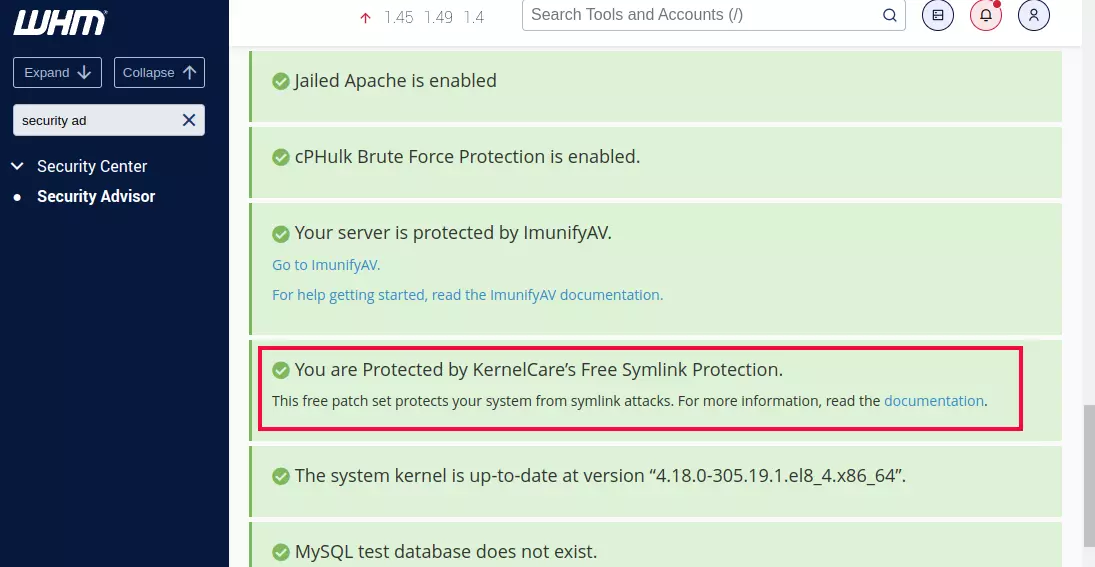
Go to WHM > Security Center > Security Advisor, and install KernelCare’s Free Symlink Protection.
If you enable SSH access for cPanel accounts, make sure it is “jailed Shell” under WHM > Account Functions > Manage Shell Access
Back to cPanel Server

Leave a Reply