To extract SSL certificate and private key from Keystore (JKS) file, run
keytool -importkeystore \
-srckeystore keystore.jks \
-destkeystore keystore.p12 \
-deststoretype PKCS12
It will ask for the new Keystore password and current Keystore password. Once you enter the password, JKS file gets converted to P12 format.
This will include all certificates in the keystone. If you only need a specific certificate, then use
-srcalias NAME_HERE
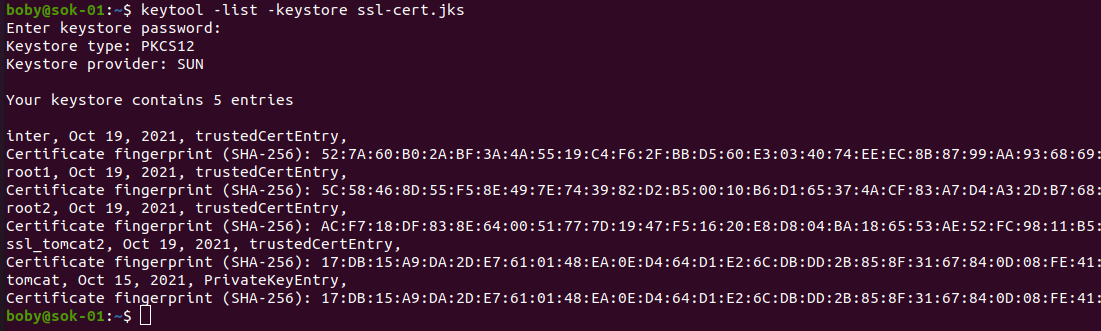
To see all certificates in a JKS file, see List contents of jks keystore file
To extract SSL certificate (Apache format), run
openssl pkcs12 -in keystore.p12 -nokeys -out cert.pem
To extract Private key, run
openssl pkcs12 -in keystore.p12 -nodes -nocerts -out key.pem
Back to keytool