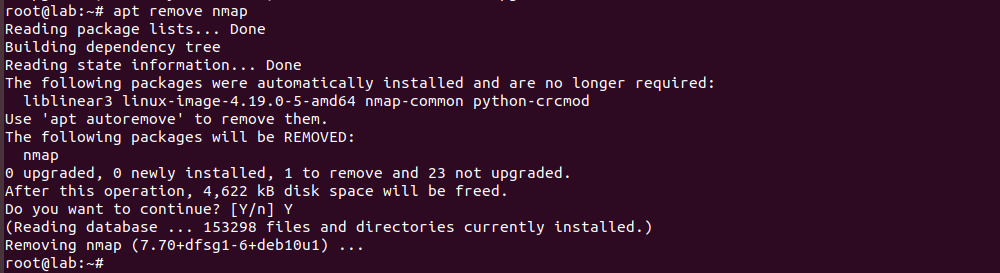
To uninstall a software on Debian server, run
apt remove PKG_NAME
Example
To all installed software with specific name, run
dpkg-query -l PKG_NAME
Example
root@lab:~# dpkg-query -l 'nginx*'
Desired=Unknown/Install/Remove/Purge/Hold
| Status=Not/Inst/Conf-files/Unpacked/halF-conf/Half-inst/trig-aWait/Trig-pend
|/ Err?=(none)/Reinst-required (Status,Err: uppercase=bad)
||/ Name Version Architecture Description
+++-==============-================-============-=========================================================
ii nginx 1.14.2-2+deb10u3 all small, powerful, scalable web/proxy server
ii nginx-common 1.14.2-2+deb10u3 all small, powerful, scalable web/proxy server - common files
un nginx-doc (no description available)
un nginx-extras (no description available)
ii nginx-full 1.14.2-2+deb10u3 amd64 nginx web/proxy server (standard version)
un nginx-light (no description available)
root@lab:~#
In above list, packages start with
ii = installed
un = currently not installed on the server
When you uninstall a package, it won’t remove all config files, such packages list as uninsalled (un). To completely delete a package, its config file and data, use
apt remove --purge PKG_NAME
Example
apt remove --purge apache2
After removing a software package, you may need to run apt autoremove to remove any unused dependency.
apt autoremove
See apt