When i run yum update on a CentOS 6 server, i get error “Invalid release/repo/arch combination/”.
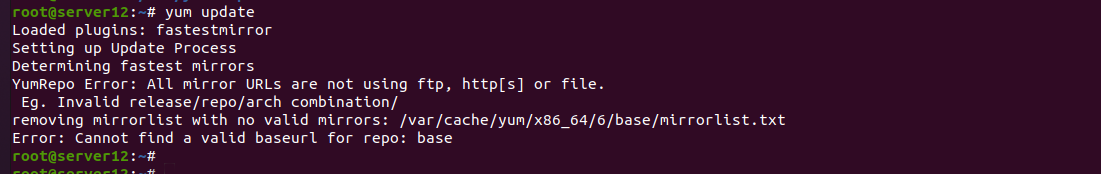
This error is due to CentOS reaching its End Of Life and no longer supported.
What you need to do is upgrade your server to the latest supported CentOS versions like CentOS 7 or CentOS 8. Converting to Oracle Linux 6 is another option, it is binary compatible with CentOS/RHEL 6, offers extended support until Jun 2024 and Indefinite Sustaining Support. If you want to convert CentOS 6 to Oracle Linux, see How to Migrate CentOS to Oracle Linux.
If you just need to fix the error, you need to go through each .repo file in the folder
/etc/yum.repos.d/
Comment out lines like
mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os&infra=$infra
Replace it with centos 6 vault repo URL
baseurl=https://vault.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
You can find modified yum repository files at
https://github.com/serverok/centos6-repo
You can replace your existing repository files inside /etc/yum.repos.d folder with files in the above git repository with following commands.
cd /etc
mv yum.repos.d yum.repos.d-old
git clone https://github.com/serverok/centos6-repo.git yum.repos.d
If you get git not found error, you may need to manually download files from the repo and place in the directory /etc/yum.repos.d/.
After this, you will be able to update your system. If you have any other repo installed, you can copy it from yum.repos.d-old folder to make it active again.
Here is the updated CentOS-Base.repo file
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/serverok/centos6-repo/main/CentOS-Base.repo
# CentOS-Base.repo
#
# The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and
# geographically close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates
# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the
# remarked out baseurl= line instead.
#
#
[base]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Base
baseurl=https://vault.centos.org/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates
baseurl=https://vault.centos.org/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras
baseurl=https://vault.centos.org/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus
baseurl=https://vault.centos.org/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#contrib - packages by Centos Users
[contrib]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Contrib
baseurl=https://vault.centos.org/centos/$releasever/contrib/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
After updating yum repo, run
yum clean all
yum makecache




