BitBucket Server alloow you to host git repositories. By default bitbucket server have url in following format
http://YOUR_IP_ADDR:7990/login
To install SSL, first point a domain to the server IP.
Install nginx
apt install nginx
Now install LetsEncrypt
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/serverok/server-setup/master/install/letsencrypt.sh
bash ./letsencrypt.sh
Get SSL in standalone mode. We use standalone mode because nginx will proxy all request to bitbucket server, so SSL validation will be difficult using nginx.
In this example, i will be using git.serverok.in, you need to replace with your actual domain.
systemctl stop nginx
certbot certonly --standalone -d git.serverok.in
Edit file
vi /usr/serverok/ssl-renew
Find
/usr/bin/certbot renew
Add before
systemctl stop nginx
Create file
vi /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/bitbucket.conf
Add
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name git.serverok.in;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/git.serverok.in/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/git.serverok.in/privkey.pem;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
client_max_body_size 1000M;
proxy_read_timeout 600s;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:7990;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name git.serverok.in;
return 301 https://git.serverok.in$request_uri;
}
Restart nginx server
systemctl restart nginx
Edit file
vi /var/atlassian/application-data/bitbucket/shared/bitbucket.properties
At end of the file, add following code
server.port=7990
server.secure=true
server.scheme=https
server.proxy-port=443
server.proxy-name=git.serverok.in
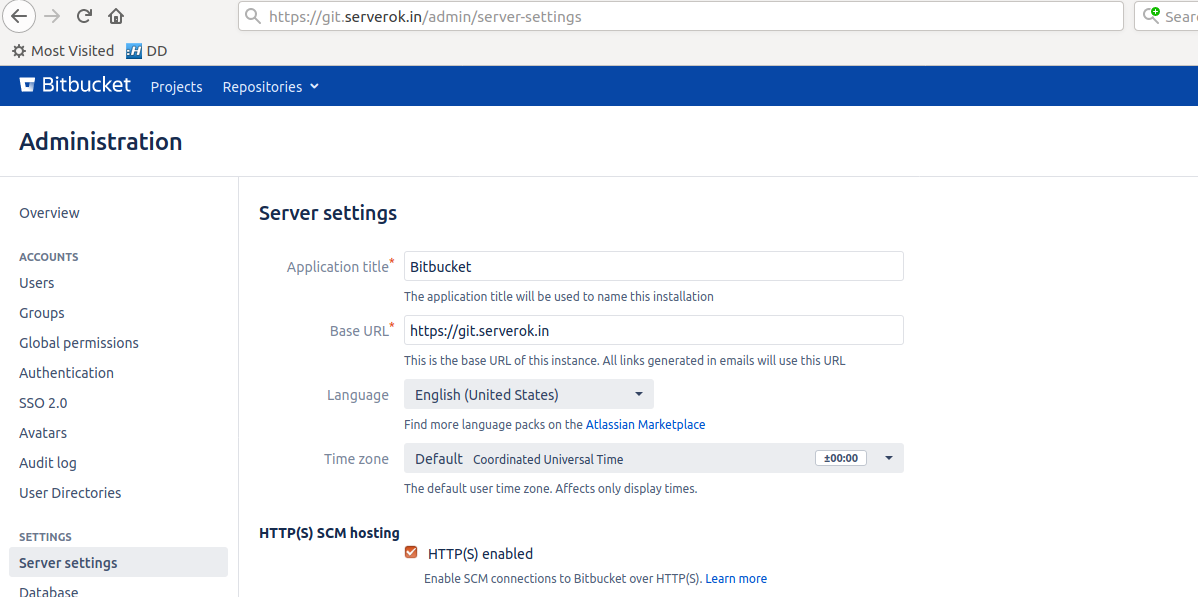
Now login to Bitbucket server, Go to Bitbucket Server administration area and click Server settings, and change Base URL to
https://git.serverok.in
Restart bitbucket server
systemctl stop atlbitbucket.service
systemctl start atlbitbucket.service