Ant Media Server is a media streaming server with WebRTC support.
https://antmedia.io
Install Ant Media Server on CentOS 8
Ant Media Server Ubuntu firewall configuration
Steaming to Anti Media Server using ffmpeg
Open Source versiong of Ant Media Server can be downloaded from
https://github.com/ant-media/Ant-Media-Server
Install Anti Media Server on Ubuntu 18.04
At the time of writing this post, latest version of Ant Media Server is ant-media-server-2.0.0-community-2.0.0-20200504_1842.zip, replace it with latest version available on github.
cd /usr/local/src
wget https://github.com/ant-media/Ant-Media-Server/releases/download/ams-v2.0.0/ant-media-server-2.0.0-community-2.0.0-20200504_1842.zip
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ant-media/Scripts/master/install_ant-media-server.sh
chmod 755 install_ant-media-server.sh
./install_ant-media-server.sh ant-media-server-2.0.0-community-2.0.0-20200504_1842.zip
After installation, you will see Ant Meida Server listens on following ports
[root@Ant-Media-Server ~]# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:5599 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1594/jsvc.exec
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:34501 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1594/jsvc.exec
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:1935 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1594/jsvc.exec
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5080 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1594/jsvc.exec
[root@Ant-Media-Server ~]#
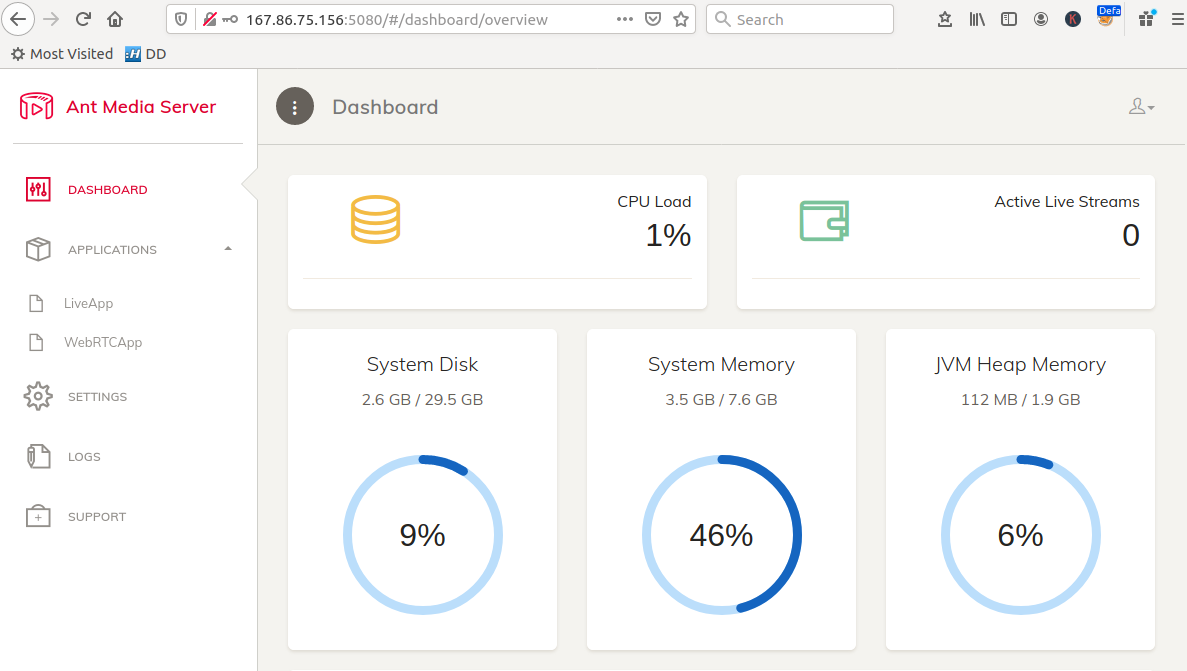
To access Ant Media Server, go to
http://your-server-ip:5080
When visiting first time, you will be asked to create a new user.
Installing SSL
To install SSL, you need to point a domain or sub domain to server IP, then run following commands
cd /usr/local/antmedia
./enable_ssl.sh -d YOUR_DOMAIN_HERE
After installation, you will be able to access site using HTTPS on following URL
https://YOUR_DOMAIN_HERE:5443
Test Video Streaming Applictaion available at
https://YOUR_DOMAIN_HERE::5443/WebRTCApp/
Manage Anti Media Server
To start/stop/restart Ant Media Server, use
systemctl start antmedia
systemctl stop antmedia
systemctl restart antmedia
Firewall
Anti Media Server use following ports
tcp:1935 - RTMP
tcp:5080 - HTTP
tcp:5443 - HTTPS
tcp:5554 - RTSP
udp:5000-65000 - WebRTC & RTSP