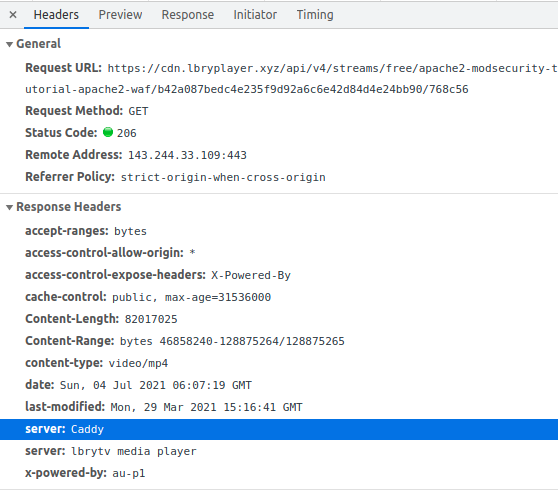
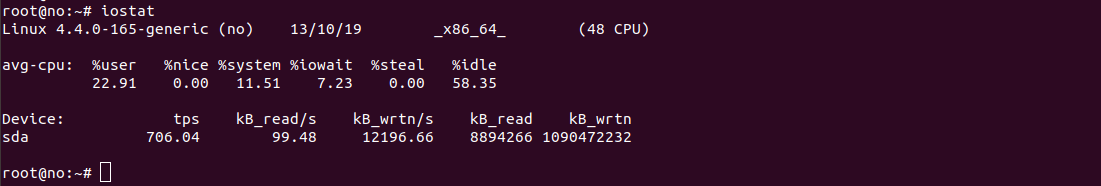
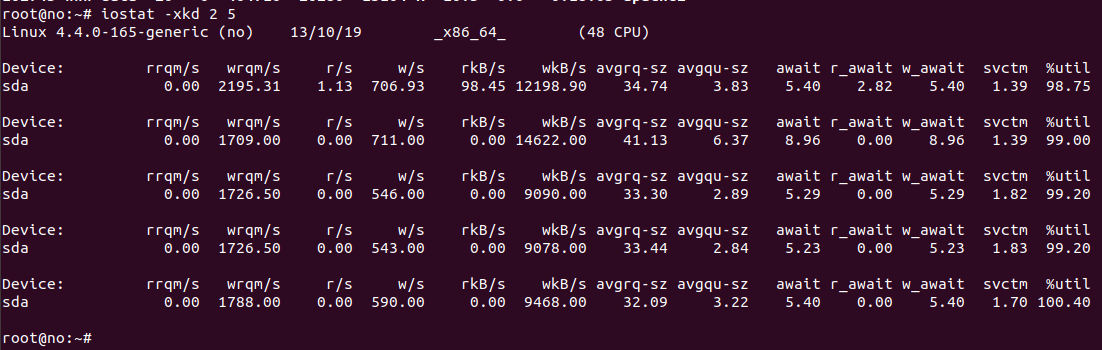
Caddy is a light weight web server written in golang. Caddy auto generate SSL for your web site using LetsEncrypt and support HTTP/2.
To instal Caddy, download latest Caddy release from github
https://github.com/caddyserver/caddy/releases/
At the time of this post, 1.3 is latest stable release, to install it, run
cd /usr/local/src
wget https://github.com/caddyserver/caddy/releases/download/v2.4.6/caddy_2.4.6_linux_amd64.tar.gz
tar xvf caddy_2.4.6_linux_amd64.tar.gz
cp /usr/local/src/caddy /usr/local/bin
chown root:root /usr/local/bin/caddy
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/caddy
Make caddy listen to privilage ports 80 and 443
setcap 'cap_net_bind_service=+ep' /usr/local/bin/caddy
If you don’t have a system user for caddy to run as, create one
groupadd -g 33 www-data
useradd -g www-data --no-user-group --home-dir /var/www --no-create-home --shell /usr/sbin/nologin --system --uid 33 www-data
Create config folder for caddy
mkdir /etc/caddy
chown -R root:root /etc/caddy
mkdir /etc/ssl/caddy
chown -R root:www-data /etc/ssl/caddy
chmod 0770 /etc/ssl/caddy
Create Caddy config file
vi /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
Add
lab.serverok.in {
root /var/www/html
}
Replace lab.serverok.in with whatever domain you need to host.
Create service file for caddy
vi /etc/systemd/system/caddy.service
Add following
[Unit]
Description=Caddy
Documentation=https://caddyserver.com/docs/
After=network.target network-online.target
Requires=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=notify
User=caddy
Group=caddy
ExecStart=/usr/bin/caddy run --environ --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
ExecReload=/usr/bin/caddy reload --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
TimeoutStopSec=5s
LimitNOFILE=1048576
LimitNPROC=512
PrivateTmp=true
ProtectSystem=full
AmbientCapabilities=CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Set permission
chown root:root /etc/systemd/system/caddy.service
chmod 644 /etc/systemd/system/caddy.service
systemctl daemon-reload
Start caddy with
systemctl start caddy
Enable caddy start on boot
systemctl enable caddy