CentOS 8 provide 2 type of ISO. One that ends with boot.iso, this is 534 MB. This only include essential files to get you started with installation. This installation method require internet connection as files needed to be downloaded from internet. Other ISO file is full install media, that is 6.6 GB in size. To install from boot.iso, download it from
http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos/8/isos/x86_64/
This page will list morrors near to you.
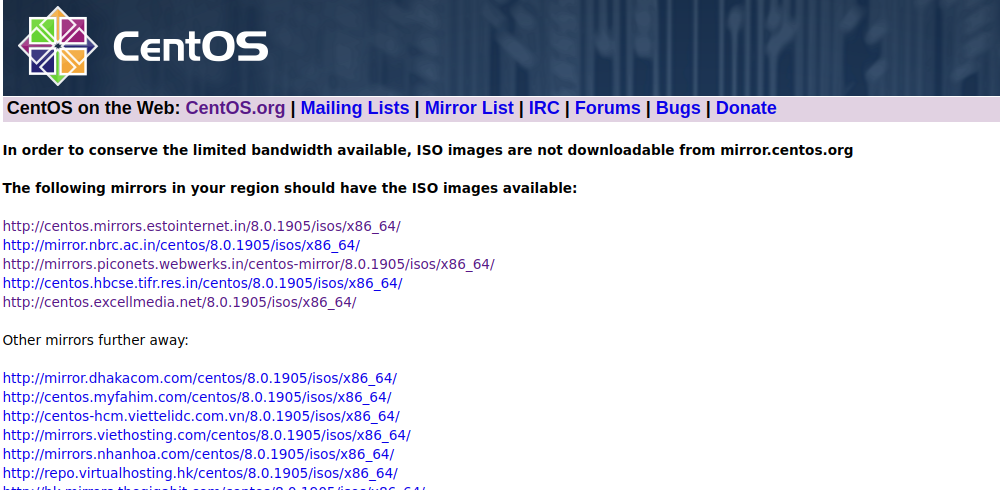
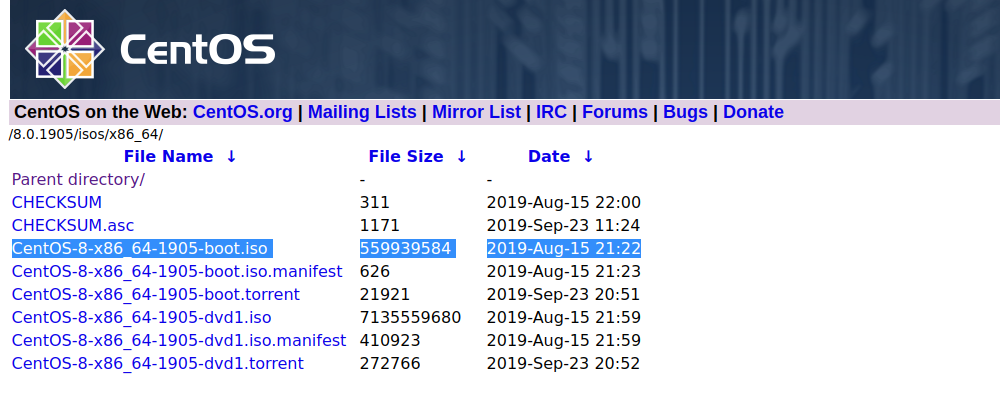
Click on any of the morror from link, on next page, you will see ISO files. Download CentOS-8-x86_64-xxxx-boot.iso
Write this ISO file into a USB drive or DVD, then boot your computer with it. You will see following screen.
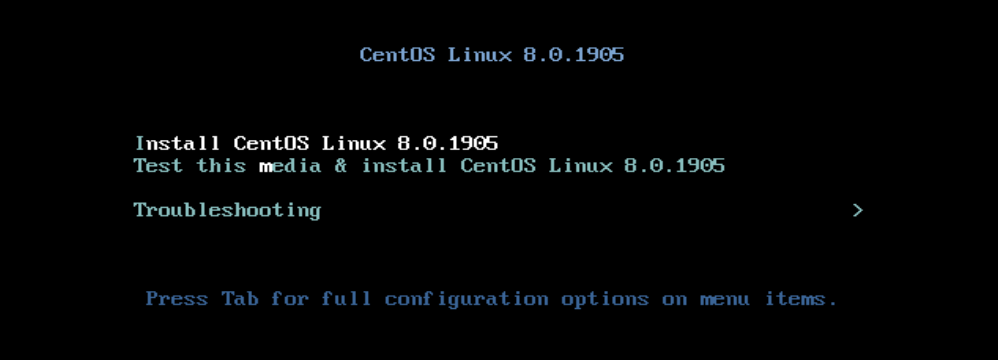
Select first or second option. 2nd option test install media for any errors. If you use USB drive, you can just select option 1 as there is less chance of media corruption compared to DVD drives.
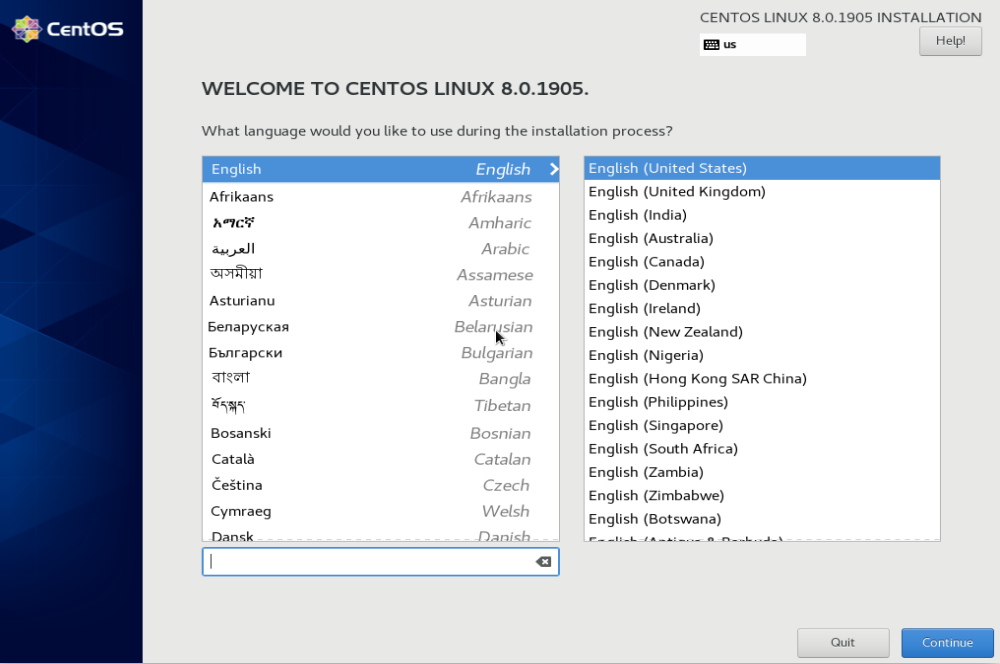
Select language, click continue.
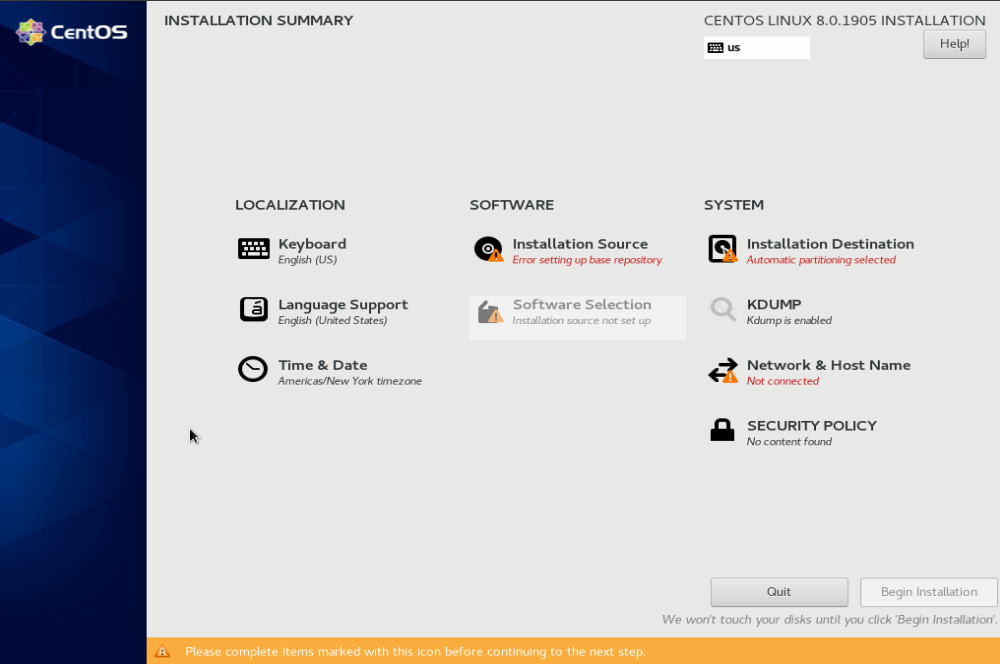
On this screen, you need to make several choices.
Installation Destination
Select the hard disk where you need CentOS 8 installed.
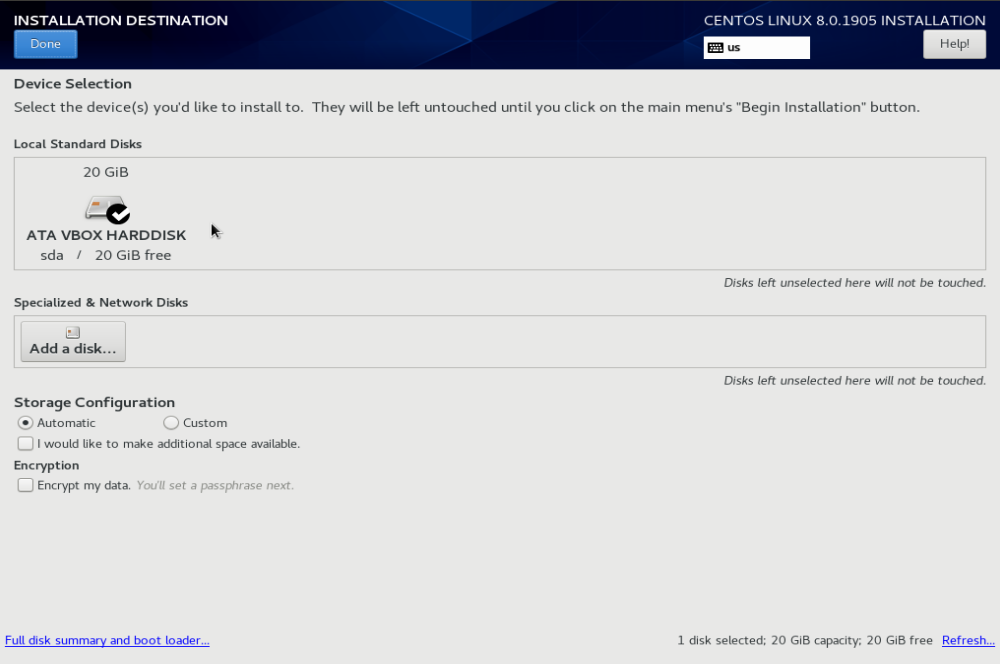
If you have an empty disk, all you need to do is click “Done”.
If your disk have existing partitions, you may need to delete it before insalling CentOS 8. If you have any data on this hard disk, always take a backup before you installing new OS.
Network & Host Name
You need to configure your network. Most of the time all you need to do is click on ON/OFF toggle on right side of the network interface.
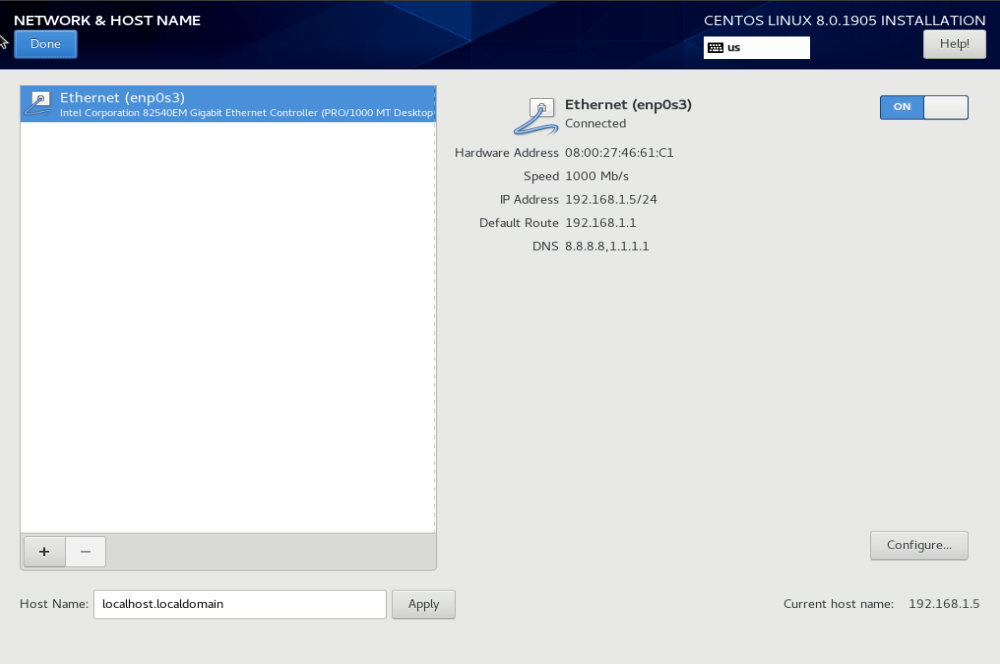
If you have DHCP on your network, you will see IP address assigned to your computer. If not, you need to manually configure networking. It is important as you will need internet to do CentOS 8 install using boot ISO file. Click Done to go back to previous screen.
Installation Source
On this page, you need to enter a CentOS mirror. You can use following URL
http://mirror.centos.org/centos/8/BaseOS/x86_64/os/
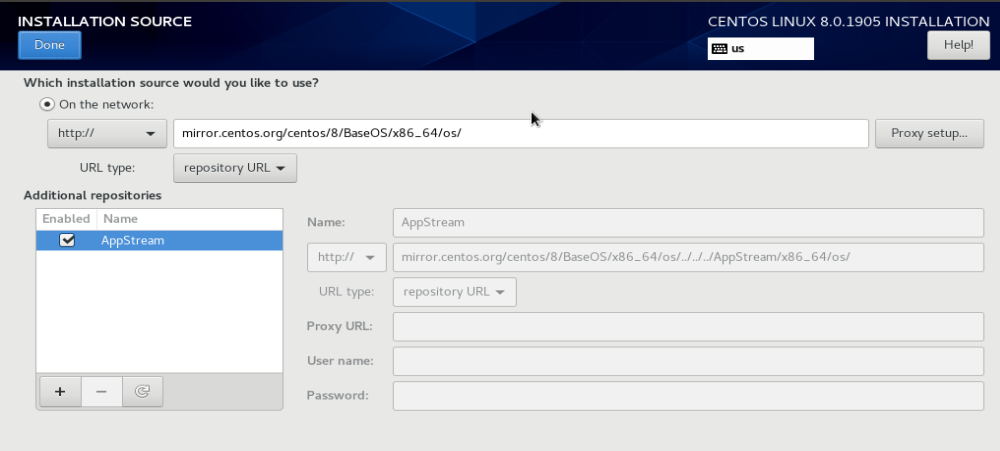
It is better to use a CentOS mirror near to you. This will make file downloads faster. In my case, i used
http://centos.mirrors.estointernet.in/8.0.1905/BaseOS/x86_64/os/
There is option to select mirror near you on this screen. But for some reason, this option did not work for me.
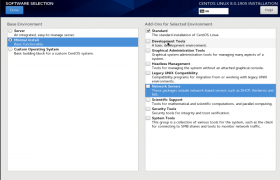
Software Slection
On this screen, you need to select software to install.
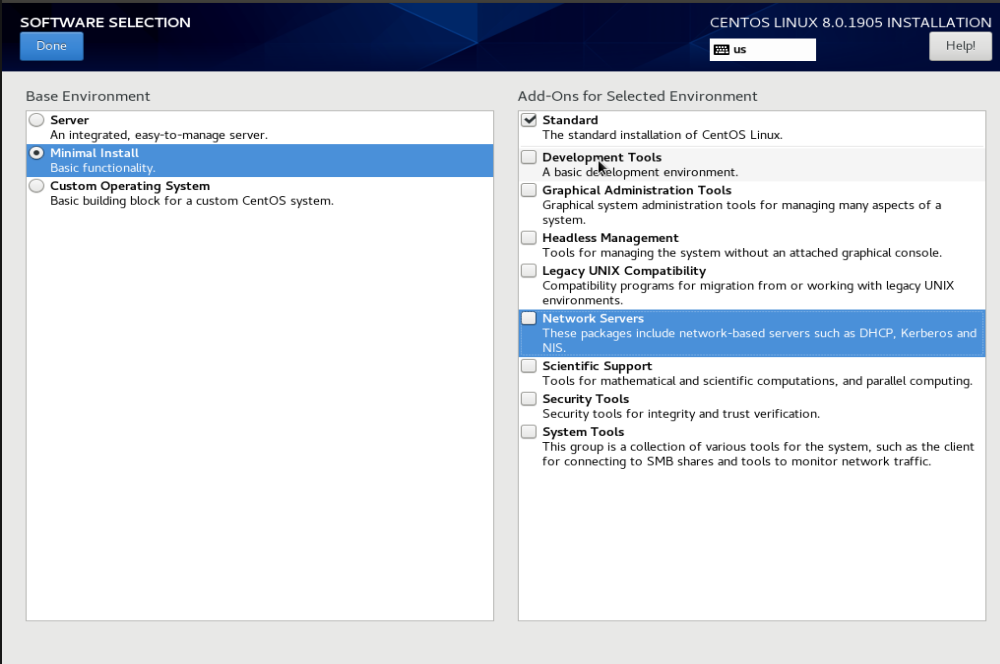
You can select if you need to install GUI or just minimal CentOS install. I selected minimal install as everything else can be installed later as needed.
Click “Done”, will take you to previous screen. Now you will see “Begin Installation” button enabled. Click on it to continue installation.
On next screen, you get option to set password. Set password for user root. You can also create a new user if required.
Installation take 15 to 30 minutes depending on your download speed. Once installation completed, you will be asked to reboot.
CentOS 8 use Kernel 4.18
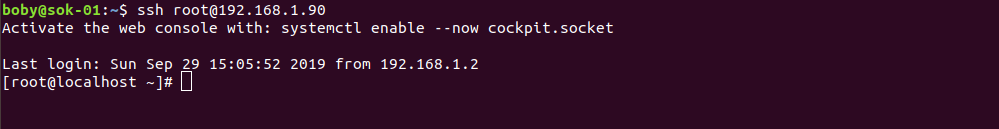
[root@192 ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: localhost.localdomain
Transient hostname: 192.168.1.5
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: 7ad955dffb89464a96918974be28795b
Boot ID: 77cd4c012cbe4b6f9c33ab7dae5ecc33
Virtualization: oracle
Operating System: CentOS Linux 8 (Core)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:8
Kernel: Linux 4.18.0-80.7.1.el8_0.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
[root@192 ~]#
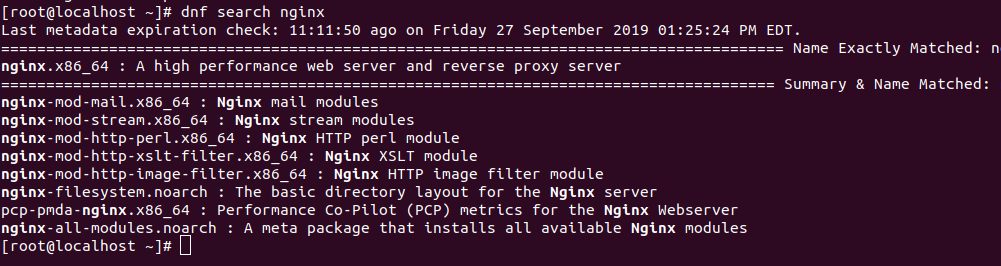
You can use both yum and dnf for installing software.