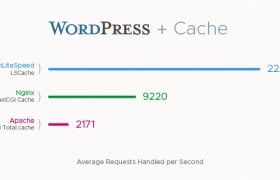
To install OpenLiteSpeed web server on CentOS, install repository for your CentOS version
For CentOS 6
rpm -Uvh http://rpms.litespeedtech.com/centos/litespeed-repo-1.1-1.el6.noarch.rpm
For CentOS 7
rpm -Uvh http://rpms.litespeedtech.com/centos/litespeed-repo-1.1-1.el7.noarch.rpm
For CentOS 8
rpm -Uvh http://rpms.litespeedtech.com/centos/litespeed-repo-1.1-1.el8.noarch.rpm
To install OpenLiteSpeed, run
yum install openlitespeed
Before you can install PHP, you need epel repository enabled with
yum install epel-release
Install PHP with
yum install lsphp73 lsphp73-common lsphp73-mysql lsphp73-gd lsphp73-process lsphp73-mbstring lsphp73-xml lsphp73-mcrypt lsphp73-pdo lsphp73-imap lsphp73-soap lsphp73-bcmath lsphp73-json lsphp73-mysqlnd
Set symlink
ln -sf /usr/local/lsws/lsphp73/bin/lsphp /usr/local/lsws/fcgi-bin/lsphp5
Start OpenLiteSpeed with
/usr/local/lsws/bin/lswsctrl start
To stop OpenLiteSpeed, run
/usr/local/lsws/bin/lswsctrl stop
By default, OpenLiteSpeed will run on port 8088
http://YOUR_SERVER_IP_HERE:8088
You can login to Admin Interface at
http://YOUR_SERVER_IP_HERE:7080 User = admin PW = 123456
By default, you see an example application. The configuration file for this is at
/usr/local/lsws/conf/vhosts/Example/vhconf.conf
Default DocumentRoot is /usr/local/lsws/Example/html. To change, edit file
vi /usr/local/lsws/conf/vhosts/Example/vhconf.conf
Find
docRoot $VH_ROOT/html/
Replace $VH_ROOT/html/ with whatever path you need. You need to restart OpenLiteSpeed to make the change go live
/usr/local/lsws/bin/lswsctrl restart