Upgrading server on a remote location is not safe unless you have KVM access. I did many Debian 8 to Debian 9 upgrade on remote server with out probem. On one server, network card name chaned from eth0 to new enp4s0 format. I had to access the server using KVM and fix network configuration by editing /etc/network/interfaces
First you need to upgrade all software on your server to latest Debian 8
apt update && apt upgrade -y && apt dist-upgrade -y
Now replace content of /etc/apt/sources.list file with following
vi /etc/apt/sources.list
Add
deb http://cloudfront.debian.net/debian/ stretch main non-free contrib
deb-src http://cloudfront.debian.net/debian/ stretch main non-free contrib
deb http://security.debian.org/debian-security stretch/updates main contrib non-free
deb-src http://security.debian.org/debian-security stretch/updates main contrib non-free
Update the software again with
apt update && apt upgrade -y && apt dist-upgrade -y
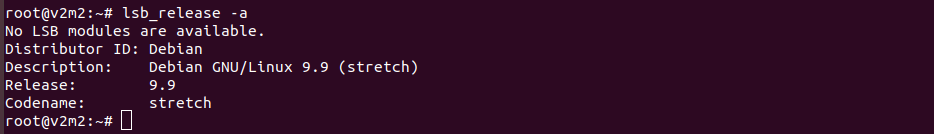
It can take some time for the upgrade to finish. Once update complete, you can check with lsb_release -a command, you will see
Remove unused packages with command
apt autoremove -y
At this stage, server stil use old debian 8 kernal.
root@v2m2:~# uname -r
3.16.0-6-amd64
root@v2m2:~#
To boot to new Debian 9 kernal, reboot the server with
reboot
After reboot, you will see new kernal.
Now Debian 10 is available. See How to upgrade Debian 9 to Debian 10