MySQL Upgrade
MariaDB
MySQL 8
MySQL 5.7
- How to Install MySQL 5.7 on Ubuntu 22.04
- How to Install MySQL 5.7 on Oracle Linux 7
- How to Install MySQL 5.7 on Amazon Linux
- How to install MySQL 5.7 on CentOS 7 Server
Back to MySQL

Back to MySQL

To reset MySQL root password on Bitnami server, first check MySQL server version you are running.
mysql --version
Create a file
vi /tmp/mysql-init
Add following text
For MySQL 5.7 or MySQL 8
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NEW_PASSWORD'; ALTER USER 'root'@'127.0.0.1' IDENTIFIED BY 'NEW_PASSWORD';
For MySQL 5.6
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD('NEW_PASSWORD') WHERE User='root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
In above code, replace NEW_PASSWORD with your new MySQL root password.
Stop MySQL
/opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh stop mysql
Reset MySQL root password by running
MySQL 5.7/MySQL 8
/opt/bitnami/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --pid-file=/opt/bitnami/mysql/data/mysqld.pid --datadir=/opt/bitnami/mysql/data --init-file=/tmp/mysql-init --lower_case_table_names=1 2> /dev/null &
If you are using MySQL 5.6 or older, run
/opt/bitnami/mysql/bin/mysqld_safe --pid-file=/opt/bitnami/mysql/data/mysqld.pid --datadir=/opt/bitnami/mysql/data --init-file=/tmp/mysql-init 2> /dev/null &
Restart MySQL
/opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh restart mysql
Now you should be able to login to MySQL server with command
mysql -u root -p'NEW_PASSWORD'
When using systemctl, you can set value for open_files_limit in my.cnf file.
Default installation of MariaDB 10 have open_files_limit set to 16384.
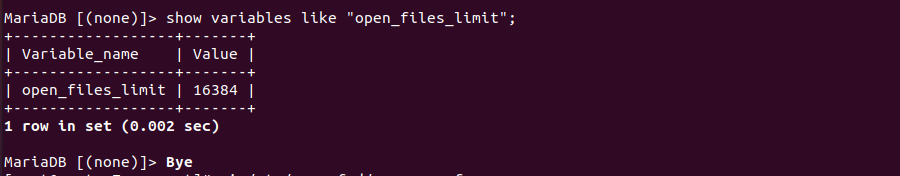
To increase value for open_files_limit, create file
mkdir /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d/ vi /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d/limitnofile.conf
Add
[Service] LimitNOFILE=1048576
Reload systemctl
systemctl daemon-reload
Restart mariadb
systemctl restart mariadb
After doing this, it get changed to 32184 instead of 1048576 we specified in limitnofile.conf
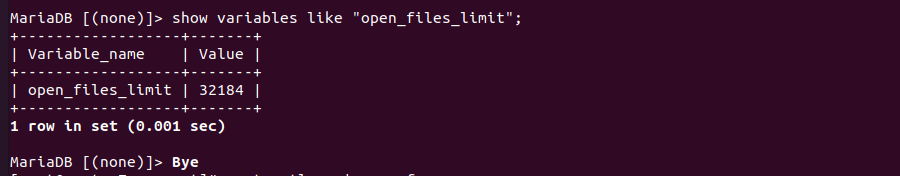
To fix this edit
On Cpanel/RHEL
vi /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
On Ubuntu/Debian
vi /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Under [mysqld], add
open_files_limit = 102400
Now after restarting MariaDB, i get 1048576 for open_files_limit.
This value depends on kernals fs.nr_open parameter. If the value is low, you can increase by editing
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Add
fs.nr_open=1048576
Then make it active with command
sysctl -p
To see current value, you can run
sysctl -a | grep fs.nr_open
To set the value for the current session, run
sysctl -w fs.nr_open=1048576
Plesk Debian 8 General error: 23 Out of resources when opening
See MySQL
When i try to repair a crashed database table, i get error
mysql> repair table visitorstats_sessions; +-------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Op | Msg_type | Msg_text | +-------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | centovacastdb.visitorstats_sessions | repair | error | Can't create new tempfile: './centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions.TMD' | | centovacastdb.visitorstats_sessions | repair | status | Operation failed | +-------------------------------------+--------+----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.01 sec) mysql>
Check the table with myisamcheck
[root@centos7 ~]# myisamchk -a /var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions Checking MyISAM file: /var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions Data records: 704545 Deleted blocks: 0 myisamchk: warning: Table is marked as crashed and last repair failed - check file-size - check record delete-chain - check key delete-chain - check index reference - check data record references index: 1 - check data record references index: 2 - check data record references index: 3 - check data record references index: 4 - check record links MyISAM-table '/var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions' is usable but should be fixed [root@centos7 ~]#
It reported some errros. To fix, run
myisamchk -r /var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions
When i run, i get following error
[root@centos7 ~]# myisamchk -r /var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions - recovering (with sort) MyISAM-table '/var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions' Data records: 704545 myisamchk: error: Can't create new tempfile: '/var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions.TMD' MyISAM-table '/var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions' is not fixed because of errors Try fixing it by using the --safe-recover (-o), the --force (-f) option or by not using the --quick (-q) flag [root@centos7 ~]#
Since the error said “Can’t create new tempfile”, i checked disk usage to make sure disk is not full. Since disk usage is not fill, i run with -f option and it worked.
[root@centos7 ~]# myisamchk -rf /var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions - recovering (with sort) MyISAM-table '/var/lib/mysql/centovacastdb/visitorstats_sessions' Data records: 704545 - Fixing index 1 - Fixing index 2 - Fixing index 3 - Fixing index 4 [root@centos7 ~]#
See MySQL Repair

I had to restore a large MySQL backup file. When restoring one of the table resulted in error. To debug the error, i wanted to split the MySQL backup taken using mysqldump into tables.
You can use csplit command to do this
csplit -s -ftable MYSQLDUMP_BACKUP_FILE_HERE "/-- Table structure for table/" {*}
This will generate files with name tableXX. First file table00 contains SQL commands used by all tables. Other files starting with table01 contains table related SQL file.
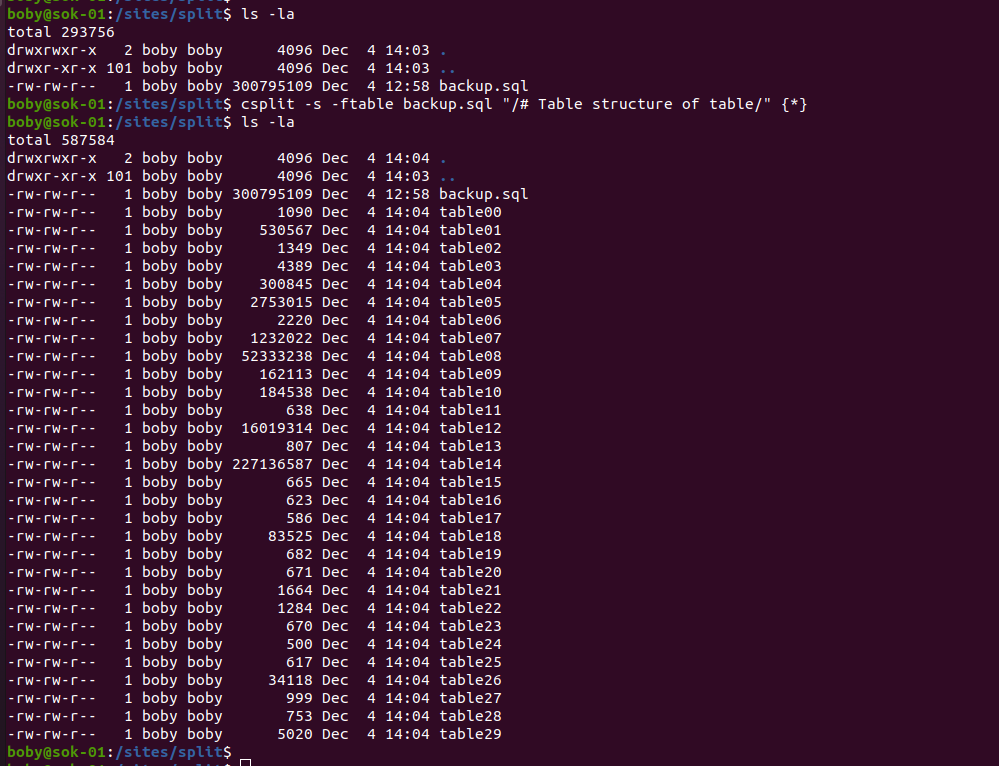
To rename the files into table name, run
for FILE in `ls -1 table*`; do TABLE=`head -n 1 $FILE | cut -d$'\x60' -f2`; mv $FILE $TABLE.sql; done
If you need to handle larger SQL file, there is a node.js project on github, that do the spliting of mysqldump file into tables.
https://github.com/vekexasia/mysqldumpsplit
See MySQL

This bash script is used to auto-restart MySQL or MariaDB database if it crashes or stops for any reason.
Create file
mkdir /usr/serverok vi /usr/serverok/mysql_monitor.sh
Add
#!/bin/bash
# Author: ServerOK
# Web: https://serverok.in/mysql-restart-bash
MYSQL_REPLY="$(mysqladmin ping)"
TIME_STAMP="$(date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")"
if [[ ! "$MYSQL_REPLY" =~ "mysqld is alive" ]]
then
systemctl restart mariadb
echo -e "${TIME_STAMP} MySQL Down\n"
fi
In the code, replace YOUR_ROOT_PW_HERE with your actual root password. If you are not using “root”, replace root with whatever username you use.
Make it executable
chmod 755 /usr/serverok/mysql_monitor.sh
Create cronjob to run the script every 5 minutes.
crontab -e
Add
*/5 * * * * /usr/serverok/mysql_monitor.sh >> /var/log/sok-mysql.log
See MySQL
To find the size of databases using SQL command, run the following SQL in MySQL prompt.
SELECT table_schema AS "Database", ROUND(SUM(data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024, 2) AS "Size (MB)" FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY table_schema;Example
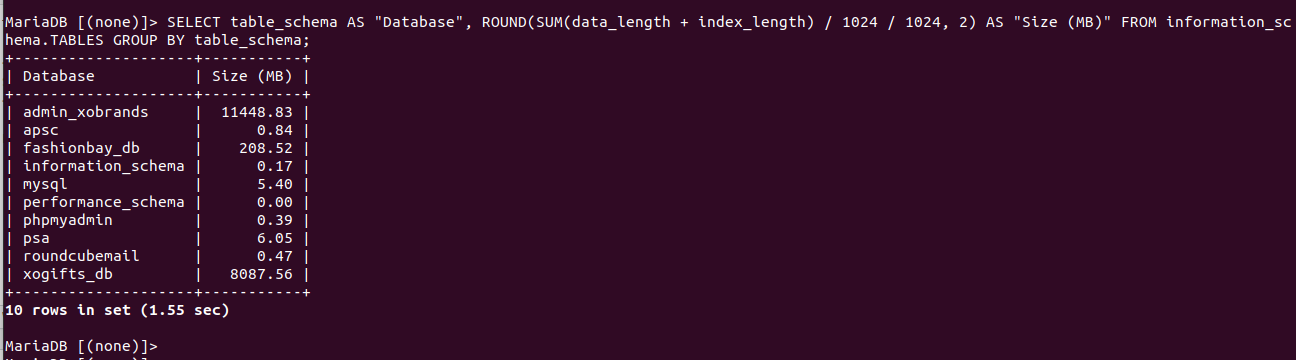
To find disk usage by tables in database, run
SELECT table_name AS "Table", round(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2) as "size (MB)" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "DB_NAME_HERE" ORDER BY data_length DESC;In the above SQL, replace DB_NAME_HERE with the actual name of the database.
Example
SELECT table_name AS "Table", round(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2) as "size (MB)" FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "xogifts_db" ORDER BY data_length DESC;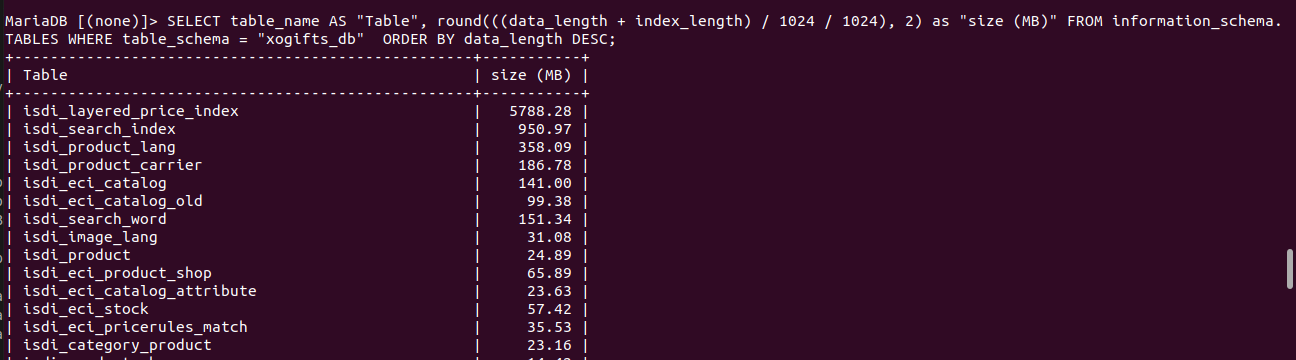
See MySQL
Percona Monitoring and Management is an Open Source monitoring software for MySQL, PostgreSQL and MongoDB.
https://www.percona.com/software/database-tools/percona-monitoring-and-management
It is based on grafana and node_exporter. You can see source code at
https://github.com/percona/pmm
Install instructions for Percona Monitoring and Management available at
https://www.percona.com/software/pmm/quickstart
See MySQL
When trying to restore a database backup to Managed DigitialOcean MySQL 8 database, i get following error
root@ocp:~# mysql -u doadmin -p'BKwsQcqEGbSV3w' -h db-sevrerok-do-user-8606188-0.b.db.ondigitalocean.com -P 25060 serverok_db < serverok_db.sql mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. ERROR 3750 (HY000) at line 223: Unable to create or change a table without a primary key, when the system variable 'sql_require_primary_key' is set. Add a primary key to the table or unset this variable to avoid this message. Note that tables without a primary key can cause performance problems in row-based replication, so please consult your DBA before changing this setting. root@ocp:~#
This is because one of the tables in your MySQL backup don't have primary key defined.
There are few ways you can fix this. Proper way is to define a primary key for the table. If this is not possible, you can set sql_require_primary_key to OFF.
To set sql_require_primary_key to OFF, edit file
vi /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
Under [mysqld] section, add
sql_require_primary_key=0
Now restart MySQL server.
systemctl restart mysql
In the case of DigitalOcean, we can't edit MySQL configuration as it is Managed MySQL Database service, What you can do is edit the MySQL backup file. Add following code to top of the file.
SET sql_require_primary_key=0;
This should be added as first SQL statement. Now do restore again, it will work.
When restoring a MySQL database, i get error
root@server:~# mysql production < db.sql ERROR 1118 (42000) at line 733: Row size too large (> 8126). Changing some columns to TEXT or BLOB may help. In current row format, BLOB prefix of 0 bytes is stored inline. root@server:~#
I installed exactly same MraiaDB version on both source and destination server. But still restring failed.
This is due to default Engine. On old server, i had
MariaDB [adrymmls]> show engines; +--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+ | Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints | +--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+ | MRG_MyISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO | | MyISAM | DEFAULT | Non-transactional engine with good performance and small data footprint | NO | NO | NO | | CSV | YES | Stores tables as CSV files | NO | NO | NO | | MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO | | Aria | YES | Crash-safe tables with MyISAM heritage | NO | NO | NO | | InnoDB | YES | Supports transactions, row-level locking, foreign keys and encryption for tables | YES | YES | YES | | PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO | | SEQUENCE | YES | Generated tables filled with sequential values | YES | NO | YES | +--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+ 8 rows in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [adrymmls]>
On new server, it had InnoDB was set as default.
MariaDB [production]> show engines; +--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+ | Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints | +--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+ | MRG_MyISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO | | CSV | YES | Stores tables as CSV files | NO | NO | NO | | MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO | | MyISAM | YES | Non-transactional engine with good performance and small data footprint | NO | NO | NO | | Aria | YES | Crash-safe tables with MyISAM heritage | NO | NO | NO | | InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, foreign keys and encryption for tables | YES | YES | YES | | PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO | | SEQUENCE | YES | Generated tables filled with sequential values | YES | NO | YES | +--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+ 8 rows in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [production]>
Solution
Edit the SQL file in a text editor. Go to the line in the error message. In this case line 733, you will see a create table statement. Go to end of this table create statement. You will see ENGINE=InnoDB, replace it with ENGINE=MyISAM.
After upgrading MariaDB on Ubuntu server, i got following error
root@server:~# mysql ERROR 1524 (HY000): Plugin 'unix_socket' is not loaded root@server:~#
Users created worked fine. Only root user had this error.
To fix, you need to enable auth_socket.so plugin.
Edit file
vi /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Find
[mysqld]
Add below
plugin-load-add = auth_socket.so
Resatrt MariaDB
systemctl restart mysqld
See MySQL
To initialize the MySQL data directory, run
mysql_install_db --user=mysqlThis will create /var/lib/mysql directory. For some versions of MySQL you can use
mysqld --initialize --user=mysqlExample
[root@panel lib]# mysql --version
mysql Ver 15.1 Distrib 10.2.31-MariaDB, for Linux (x86_64) using readline 5.1
[root@panel lib]# mysql_install_db --user=mysql
Installing MariaDB/MySQL system tables in '/var/lib/mysql' ...
OK
To start mysqld at boot time you have to copy
support-files/mysql.server to the right place for your system
PLEASE REMEMBER TO SET A PASSWORD FOR THE MariaDB root USER !
To do so, start the server, then issue the following commands:
'/usr/bin/mysqladmin' -u root password 'new-password'
'/usr/bin/mysqladmin' -u root -h panel.topnews.us password 'new-password'
Alternatively you can run:
'/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation'
which will also give you the option of removing the test
databases and anonymous user created by default. This is
strongly recommended for production servers.
See the MariaDB Knowledgebase at http://mariadb.com/kb or the
MySQL manual for more instructions.
You can start the MariaDB daemon with:
cd '/usr' ; /usr/bin/mysqld_safe --datadir='/var/lib/mysql'
You can test the MariaDB daemon with mysql-test-run.pl
cd '/usr/mysql-test' ; perl mysql-test-run.pl
Please report any problems at http://mariadb.org/jira
The latest information about MariaDB is available at http://mariadb.org/.
You can find additional information about the MySQL part at:
http://dev.mysql.com
Consider joining MariaDB's strong and vibrant community:
Get Involved
[root@panel lib]# See MySQL