To auto upgrade software packages in Ubuntu/Debian, install
apt install -y unattended-upgrades
Edit
vi /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgrades
In this file, you can configure various settings.
See apt
To auto upgrade software packages in Ubuntu/Debian, install
apt install -y unattended-upgrades
Edit
vi /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgrades
In this file, you can configure various settings.
See apt
PowerDNS is an OpenSource DNS server.
Update apt repo
apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y
On Ubuntu, systemd-resolved listen to port 53. This is a local DNS resolver, we need to stop this service before we can install PowerDNS.
systemctl disable systemd-resolved systemctl stop systemd-resolved rm -f /etc/resolv.conf echo "nameserver 1.1.1.1" > /etc/resolv.conf echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" >> /etc/resolv.conf
To install PowerDNS with MySQL backend, run
apt install pdns-server pdns-backend-mysql
Since we are using MySQL backend to store DNS zones, we need to install MySQL database.
apt install mariadb-server
Login to MySQL, create a database and user.
mysql CREATE DATABASE powerdns; GRANT ALL ON powerdns.* TO 'powerdns'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YOUR_MYSQL_PW_HERE';
Restore database scheme provided by powerdns
mysql powerdns < /usr/share/pdns-backend-mysql/schema/schema.mysql.sql
You can see this scheme in PowerDNS documentation.
Configure PowerDNS to use MySQL backend
vi /etc/powerdns/pdns.d/mysql.conf
Add following content
# MySQL Configuration # Launch gmysql backend launch+=gmysql # gmysql parameters gmysql-host=localhost gmysql-port=3306 gmysql-dbname=powerdns gmysql-user=powerdns gmysql-password=YOUR_MYSQL_PW_HERE gmysql-dnssec=yes # gmysql-socket=
Restart PowerDNS
systemctl restart pdns
If PowerDNS started properly, you will see it listening to port 53. You can verify with command netstat -lntp

In above picture, you will see PowerDNS listen to port 53 and 8081. Port 8081 is API port, you won't see it unless you enabled it.
To verify PowerDNS is running, you can use command
root@vultr:~# dig @127.0.0.1 ; <<>> DiG 9.16.1-Ubuntu <<>> @127.0.0.1 ; (1 server found) ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: REFUSED, id: 63898 ;; flags: qr rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1 ;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1232 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;. IN NS ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1) ;; WHEN: Mon Oct 12 06:53:40 UTC 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 28 root@vultr:~#
Back to PowerDNS
On Ubuntu, some times notifications steal focus from current application. This annoying when you are working on terminal. This is due to start focus feature of gnome when your mouse is over the notification area.
boby@sok-01:~$ gsettings get org.gnome.desktop.wm.preferences focus-new-windows 'smart' boby@sok-01:~$
We need to change the value of focus-new-windows from smart to strict. This can be done with command
gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.wm.preferences focus-new-windows 'strict'

On Debian and Ubuntu servers, you can download a package using apt download command.
apt download PKG_NAME

Package will get downloaded to current working directory. Better do this to /tmp to avoid permission errors.
If you want to download package and dependencies, then use
apt-get install --download-only PKG_NAME
This will download the package and all dependency, store it in folder /var/cache/apt/archives.
If you need to remove downloaded packages, run
apt clean
Seeapt-get
To block packages from upgrading, you can use command apt-mark hold.
apt-mark hold PKG_NAME
Example
apt-mark hold libtomcat8-java tomcat8 tomcat8-admin tomcat8-common
To list packages that are on hold, run
root@ip-172-26-8-193:~# apt-mark showhold libtomcat8-java tomcat8 tomcat8-admin tomcat8-common root@ip-172-26-8-193:~#
If you want to remove block, you can use apt-mark unhold command.
apt-mark unhold libtomcat8-java tomcat8 tomcat8-admin tomcat8-common
See apt
On Ubuntu/Debian server, apache run as user www-data. When you install Apache web server on your local computer for developement purpose, it may be easier to run Apache as your user. If you run Apache as www-data user, you will need to chmod folders 777 for yoru web application to write to a folder like file upload, creating log files etc..
To change Apache user, edit file
vi /etc/apache2/envvars
Find and replace www-data with your user name. You can do this with following sed command
sed -i "s/www-data/USERNAME/g" /etc/apache2/envvars chown -R USERNAME:USERNAME /var/lib/php
To install wireguard VPN on ubuntu, run
apt update apt install software-properties-common apt install linux-headers-$(uname -r) add-apt-repository ppa:wireguard/wireguard apt-get update apt-get install wireguard
cd /etc/wireguard umask 077 wg genkey > privatekey cat privatekey | wg pubkey > publickey
You can generate wireguard configuration using
On my local computer, i have installed openssh-server, but i don’t want it always enabled.
To disable openssh-server from auto start on boot, run
systemctl disable ssh
Example
root@lab:~# systemctl disable ssh Synchronizing state of ssh.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install disable ssh Removed /etc/systemd/system/sshd.service. Removed /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ssh.service. root@lab:~#
If you want to start ssh server on boot, run systelctl enable ssh
root@lab:~# systemctl enable ssh Synchronizing state of ssh.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable ssh Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/sshd.service → /lib/systemd/system/ssh.service. Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ssh.service → /lib/systemd/system/ssh.service. root@lab:~#
See Ubuntu
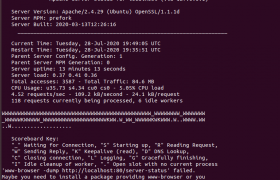
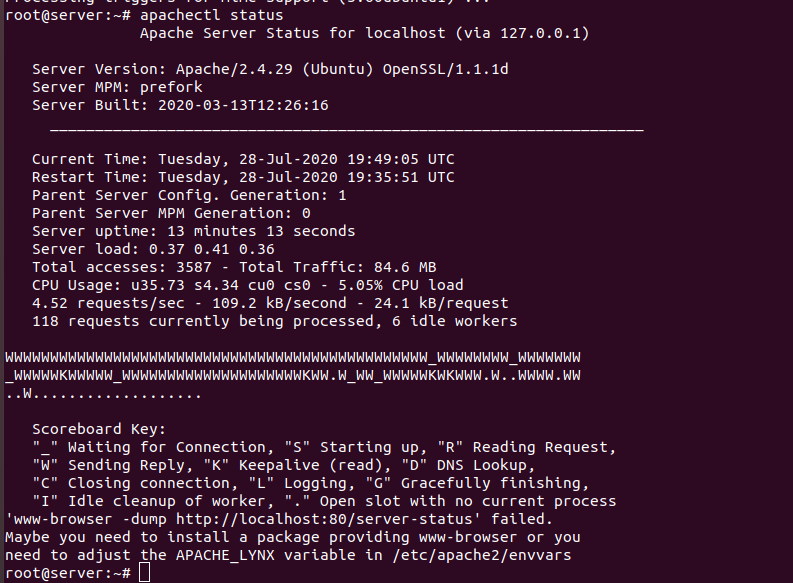
On a Ubuntu server, run i run apachectl status, i get following error.
root@server:~# apachectl status /usr/sbin/apachectl: 113: /usr/sbin/apachectl: www-browser: not found 'www-browser -dump http://localhost:80/server-status' failed. Maybe you need to install a package providing www-browser or you need to adjust the APACHE_LYNX variable in /etc/apache2/envvars root@server:~#
To fix error, install lynx text based browser.
apt install lynx
After installing lunx, apachectl status started working.
See Apache
After upgrading MariaDB on Ubuntu server, i got following error
root@server:~# mysql ERROR 1524 (HY000): Plugin 'unix_socket' is not loaded root@server:~#
Users created worked fine. Only root user had this error.
To fix, you need to enable auth_socket.so plugin.
Edit file
vi /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Find
[mysqld]
Add below
plugin-load-add = auth_socket.so
Resatrt MariaDB
systemctl restart mysqld
See MySQL
When running apt update, i get following error
W: An error occurred during the signature verification. The repository is not updated and the previous index files will be used. GPG error: http://packages.cloud.google.com cloud-sdk-jessie InRelease: The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY 6A030B21BA07F4FB
To fix this error, run
apt-key adv --keyserver keys.gnupg.net --recv-keys 6A030B21BA07F4FB