When running man command on a debian server, i get error
root@lab:~# man sftp -bash: man: command not found root@lab:~#
This is because man-db package not installed on the server. To fix, install man-db package with
apt install man-db
See Errors
When running man command on a debian server, i get error
root@lab:~# man sftp -bash: man: command not found root@lab:~#
This is because man-db package not installed on the server. To fix, install man-db package with
apt install man-db
See Errors
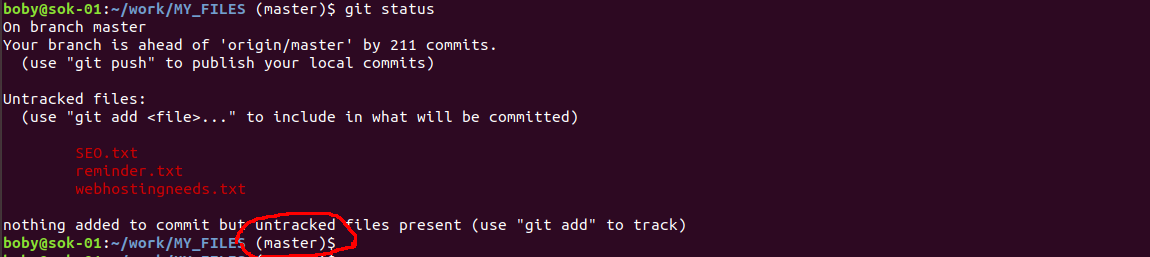
When working with git, to avoid accidental commit to wrong branch, it will be better if terminal show the branch name you are currently in.

To display “git branch” in terminal, edit .bashrc
vi ~/.bashrc
Add following code to end of the file.
# Show git branch in command promt if git repo
show_git_branch() {
git branch 2> /dev/null | sed -e '/^[^*]/d' -e 's/* \(.*\)/ (\1)/'
}
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]$(show_git_branch)\$ '
You will need to restart terminal after making changes to ~/.bashrc file or run
source ~/.bashrc
See Git
Reverse-DNS/PTR is used by mail servers. It is used to map an IP address to FQDN or hostname.
To find Reverse DNS record for an IP address, run
nslookup IP_ADDR_HERE
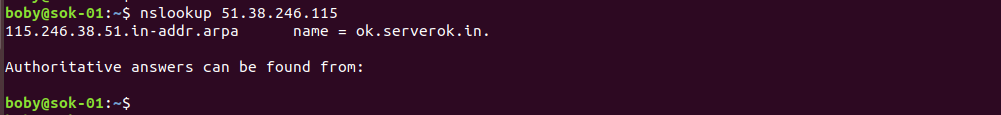
In this example IP 51.38.246.115 have a Reverse DNS record ok.serverok.in
You can also use dig command to find PTR record for an IP address.
dig -x IP_ADDR_HERE dig +short -x IP_ADDR_HERE

host IP_ADDR_HERE

See DNS
To disable SELinux
sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config setenforce 0
edit file
vi /etc/selinux/config
Find
SELINUX=enforcing
Replace with
SELINUX=disabled
Reboot the server with
reboot
You can disable selinux for current session by running command
setenforce 0
See SELinux
For linux to show hidden files when you type ls command
Edit ~/.bashrc
vi /root/.bashrc
Add line
alias ls='ls -la --color'
Save and exit. Now you need to re login to SSH to see the hidden files when you type “ls”
After editing the file will look like
[root@194 ~]# cat /root/.bashrc
# .bashrc
# User specific aliases and functions
alias rm='rm -i'
alias cp='cp -i'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias ls='ls -la --color'
# Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
[root@194 ~]#
Here is some example of using curl to login to site, use cookie to do further requests.
curl -k --cookie-jar ./cookies_hotfile --data "returnto=%2F&user=USERNAME_HERE&pass=PASSWORD_HERE" http://site.com/login.php curl -L -O --cookie ./cookies_hotfile http://site.com/dl/5222/4444/file.zip.html
See curl
chown command is ued to change ownership of a file or folder
In this example ownership of folder public_html to username and group specified.
chown -R username:group public_html
-R used for recursively change ownership, that is all files and folders inside the folder also get the new ownership.
See Linux Commands
yum install at
Enable atd
[root@server12 ~]# service atd status atd is stopped [root@server12 ~]# chkconfig --list | grep atd atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off [root@server12 ~]# service atd start Starting atd: [ OK ] [root@server12 ~]#
Setting Job
[root@server12 ~]# echo "/sbin/shutdown -h now" | at 21:15 16.02.2017 job 1 at 2017-02-16 21:15 [root@server12 ~]# atq 1 2017-02-16 21:15 a root [root@server12 ~]#
Deleting at job
[root@server12 ~]# atq 1 2017-02-16 21:15 a root [root@server12 ~]# man atq [root@server12 ~]# atrm 1 [root@server12 ~]# atq [root@server12 ~]#
See linux commands
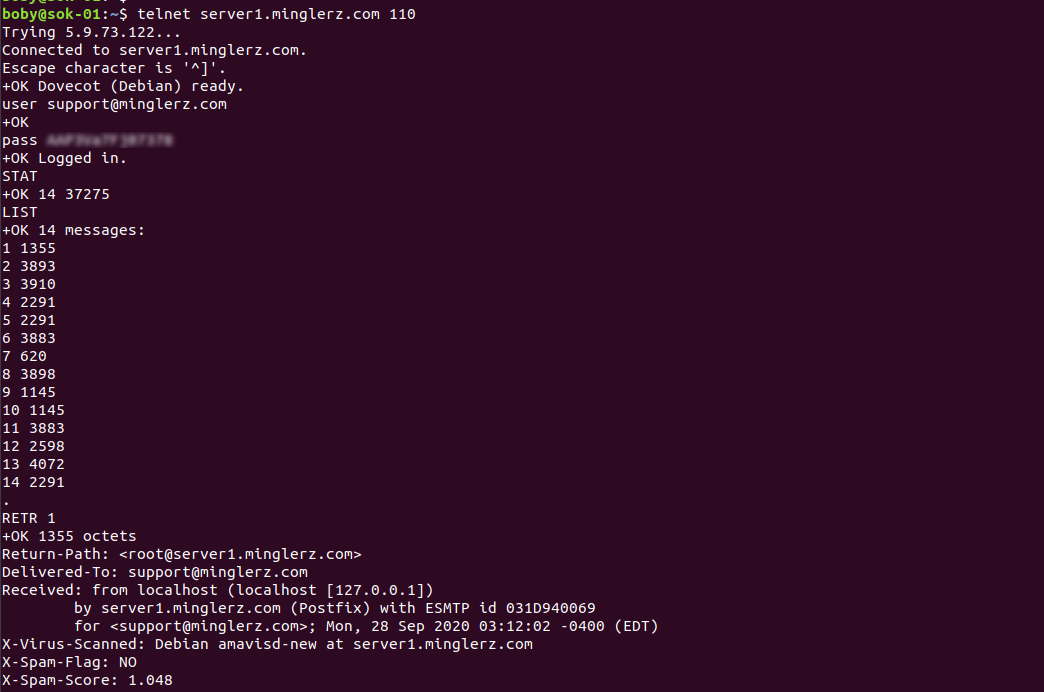
To test if pop3 mailbox work using telnet, use
telnet MAIL_SERVER_IP 110 user YOUR_EMAIL_ADDRESS pass YOUR_EMAIL_PASSWORD
Once logged in, you can use commands like
STAT LIST RETR DELE RSET TOP QUIT
See telnet
To auto upgrade software packages in Ubuntu/Debian, install
apt install -y unattended-upgrades
Edit
vi /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgrades
In this file, you can configure various settings.
See apt
PowerDNS is an OpenSource DNS server.
Update apt repo
apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y
On Ubuntu, systemd-resolved listen to port 53. This is a local DNS resolver, we need to stop this service before we can install PowerDNS.
systemctl disable systemd-resolved systemctl stop systemd-resolved rm -f /etc/resolv.conf echo "nameserver 1.1.1.1" > /etc/resolv.conf echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" >> /etc/resolv.conf
To install PowerDNS with MySQL backend, run
apt install pdns-server pdns-backend-mysql
Since we are using MySQL backend to store DNS zones, we need to install MySQL database.
apt install mariadb-server
Login to MySQL, create a database and user.
mysql CREATE DATABASE powerdns; GRANT ALL ON powerdns.* TO 'powerdns'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YOUR_MYSQL_PW_HERE';
Restore database scheme provided by powerdns
mysql powerdns < /usr/share/pdns-backend-mysql/schema/schema.mysql.sql
You can see this scheme in PowerDNS documentation.
Configure PowerDNS to use MySQL backend
vi /etc/powerdns/pdns.d/mysql.conf
Add following content
# MySQL Configuration # Launch gmysql backend launch+=gmysql # gmysql parameters gmysql-host=localhost gmysql-port=3306 gmysql-dbname=powerdns gmysql-user=powerdns gmysql-password=YOUR_MYSQL_PW_HERE gmysql-dnssec=yes # gmysql-socket=
Restart PowerDNS
systemctl restart pdns
If PowerDNS started properly, you will see it listening to port 53. You can verify with command netstat -lntp

In above picture, you will see PowerDNS listen to port 53 and 8081. Port 8081 is API port, you won't see it unless you enabled it.
To verify PowerDNS is running, you can use command
root@vultr:~# dig @127.0.0.1 ; <<>> DiG 9.16.1-Ubuntu <<>> @127.0.0.1 ; (1 server found) ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: REFUSED, id: 63898 ;; flags: qr rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1 ;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1232 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;. IN NS ;; Query time: 0 msec ;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1) ;; WHEN: Mon Oct 12 06:53:40 UTC 2020 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 28 root@vultr:~#
Back to PowerDNS