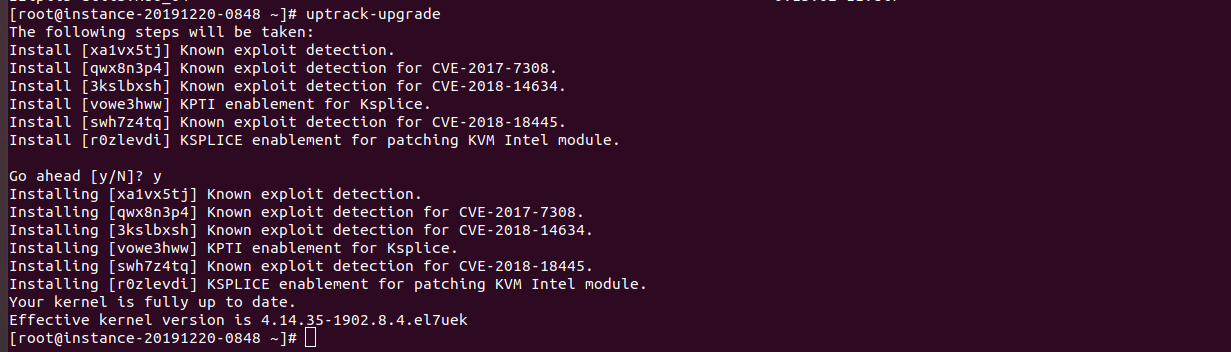
Oracle Linux come with Ksplice, it allow you to upgrade Kernel with out rebooting.
To update kernel, run
uptrack-upgrade
Example
Oracle Linux come with Ksplice, it allow you to upgrade Kernel with out rebooting.
To update kernel, run
uptrack-upgrade
Example

ClamAV is provided by the EPEL repo. Install epel repo
yum install -y epel-release
Install ClamAV with
yum install clamav
Back to ClamAV

On my computer running Ubuntu 18.04, MriaDB stopped working. PHP application i run on my computer failed with error
SQLSTATE[42S02]: Base table or view not found: 1146 Table 'ok_test.feeds' doesn't exist (SQL: select * from `feeds` where `processed` = 0)
Application can’t find the table. So i tried to login to MySQL and see if table is there or not. But i get error
boby@sok-01:~$ mysql Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 2504 Server version: 10.2.30-MariaDB-1:10.2.30+maria~bionic-log mariadb.org binary distribution Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; ERROR 1018 (HY000): Can't read dir of '.' (errno: 24 "Too many open files") MariaDB [(none)]>
Next i checked if this is due to any MySQL upgrade. I found MySQL got updated today
root@sok-01:~# grep mariadb /var/log/dpkg.log 2019-12-13 08:02:46 status triggers-pending mariadb-server-10.2:amd64 1:10.2.29+maria~bionic 2019-12-13 08:02:46 upgrade mariadb-common:all 1:10.2.29+maria~bionic 1:10.2.30+maria~bionic 2019-12-13 08:02:46 status half-configured mariadb-common:all 1:10.2.29+maria~bionic 2019-12-13 08:02:46 status unpacked mariadb-common:all 1:10.2.29+maria~bionic 2019-12-13 08:02:46 status half-installed mariadb-common:all 1:10.2.29+maria~bionic
To fix this error, run
systemctl edit mysql
This wil open a text editor. Add following
[Service] LimitNOFILE=8192
Save and quit the editor. Restart MaraDB with
systemctl restart mysql
MySQL will work properly now. systemctl edit mysql will create file /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service.d/override.conf
root@sok-01:~# cat /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service.d/override.conf [Service] LimitNOFILE=8192 root@sok-01:~#
OpenLiteSpeed is an open-source version of the popular commercial web server LiteSpeed. OpenLiteSpeed contains all of the essential features found in LiteSpeed Enterprise.
You can get OpenLiteSpeed from
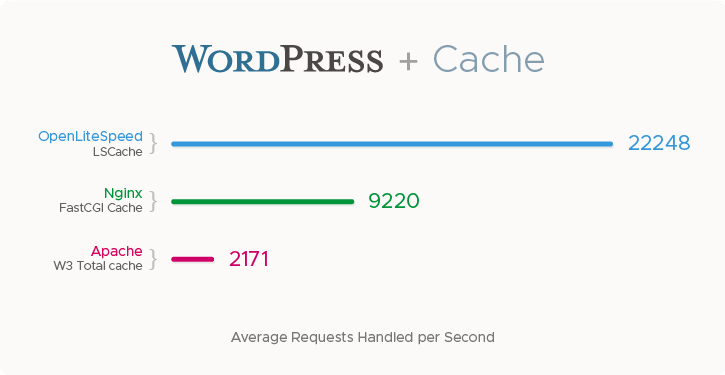
Here is a benchmark from the OpenLiteSpeed website that compares OpenLiteSpeed with Nginx.
OpenLiteSpeed configuration file
/usr/local/lsws/conf/httpd_config.confTo start/stop/restart, use
/usr/local/lsws/bin/lswsctrl start
/usr/local/lsws/bin/lswsctrl stop
/usr/local/lsws/bin/lswsctrl restart
/usr/local/lsws/bin/lswsctrl statusOpenLiteSpeed web server stores cache in directory /usr/local/lsws/cachedata. This can grow big over time. You can delete this folder to free up space or move it to another partition with free disk space and create a symlink.
To set/reset the WebAdmin password, run
/usr/local/lsws/admin/misc/admpass.shUpdate OpenLiteSpeed
/usr/local/lsws/admin/misc/lsup.sh -v 1.8.1You can login to WebAdmin at
https://server-ip:7080Linux whois command is used to find who owns a domain or IP address.
To see information about a domain, use
whois DOMAIN_NAME_HERE
Example
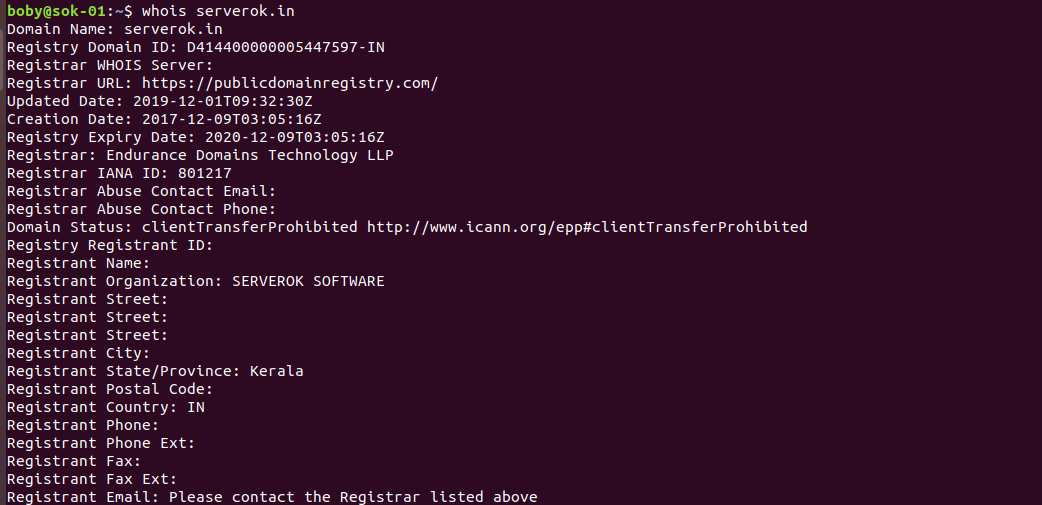
To find information about an IP address, use
whois IP_ADDR_HERE
Example
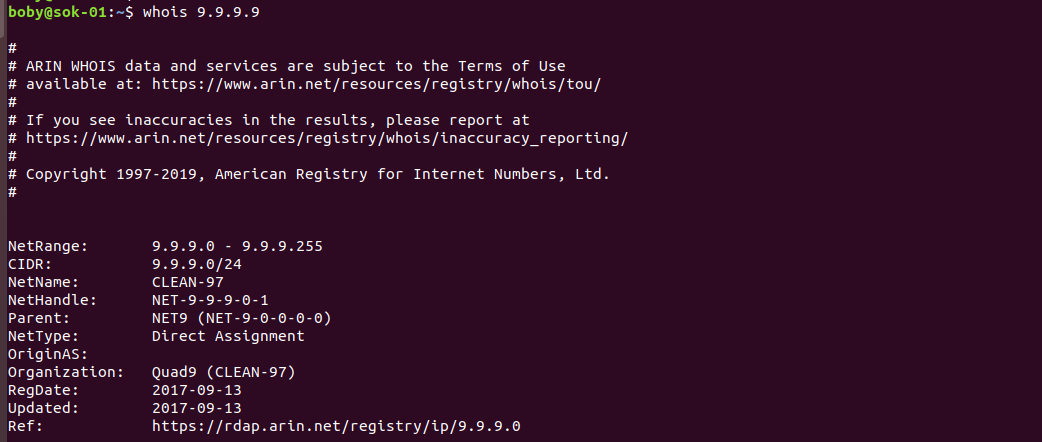
Related Posts

To regenerate grub config on CentOS 7, run
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
If you use UEFI, run
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/centos/grub.cfg
OVH CentOS 7 server grub rescue prompt
Back to grub

To reinstall a package with yum, run
yum reinstall PKG_NAME
Example
yum reinstall kernel
Prometheus is used an open source software, that can collect metrics and alerting.
You can download latest version oof Prometheus from
https://prometheus.io/download/
Create a user
useradd --no-create-home --system --shell /bin/false prometheus
Download and Install prometheus
cd /usr/local/src wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.31.0-rc.1/prometheus-2.31.0-rc.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz tar xvf prometheus-2.31.0-rc.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz cd prometheus-2.31.0-rc.1.linux-amd64 mv prometheus /usr/local/bin/ mv promtool /usr/local/bin/ mkdir /etc/prometheus mkdir /var/lib/prometheus mv consoles /etc/prometheus mv console_libraries /etc/prometheus mv prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus chown prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus chown prometheus:prometheus /var/lib/prometheus
Create a service file
vi /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
Add following content
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
User=prometheus
Group=prometheus
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \
--config.file /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
--storage.tsdb.path /var/lib/prometheus/ \
--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \
--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Enable prometheus to start on boot
systemctl enable prometheus
Start prometheus
systemctl start prometheus systemctl status prometheus
Prometheus runs on port 9090, you can access promethus at
http://YOUR_SERVER_IP:9090/graph
It will look like
Prometheus have some basic graphing features, but you can’t use it for monitoring. To create dash board and monitor, you need to use grafana.
Node Exporter is used to collect data from servers. All monitored servers need Node Exporter installed. You can download latest version of NodeExporter from
https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases
Lets create a user for Node Exporter to run
useradd --no-create-home --system --shell /bin/false node_exporter
Install Node Exporter
cd /usr/local/src wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.2.2/node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz tar xvf node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz cd /usr/local/src/node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64/ mv node_exporter /usr/local/bin/
Create a systemd service file for node exporter
vi /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.service
Add
[Unit] Description=Node Exporter Wants=network-online.target After=network-online.target [Service] User=node_exporter Group=node_exporter Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/node_exporter [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Enable and start Node Exporter
systemctl enable node_exporter systemctl start node_exporter systemctl status node_exporter
Node Exporter run on port 9100 and expose system metrics on url
http://SERVER_IP:9100/metrics
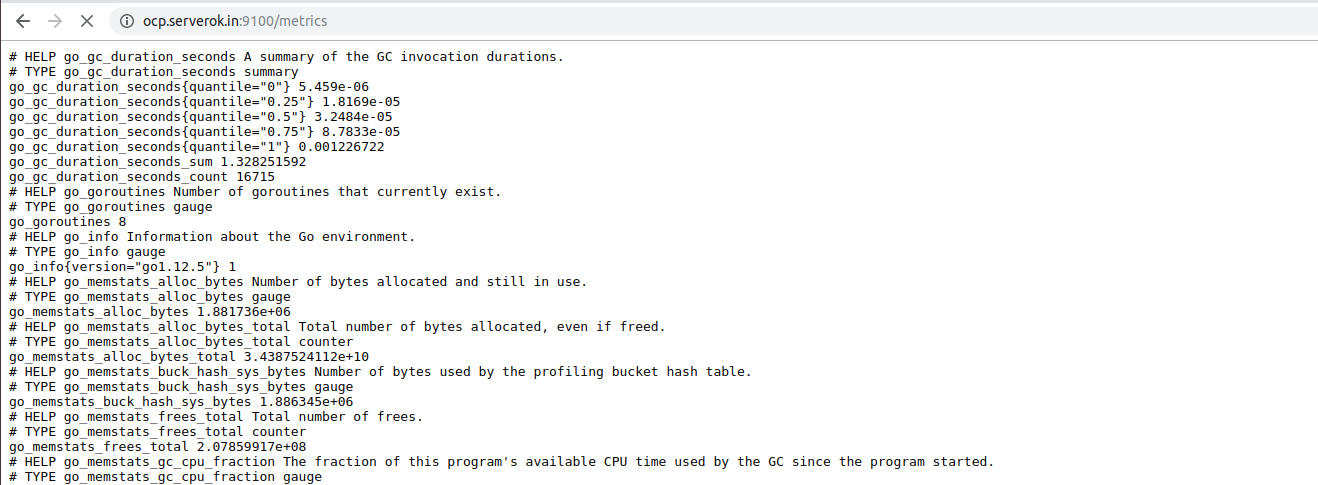
Once Node Exporter installed on a server, you need to tell Prometheus to get data from the Node Exporter you just installed. To do this, edit Prometheus configuration file.
vi /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Add following
- job_name: 'node_exporter'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['SERVER_IP:9100']
To monitor multiple servers, you can dd more servers in targets line. Here is an example config
https://gist.github.com/serverok/83a622e7577da36384f87fe60c9930af/raw
Restart prometheus
systemctl restart prometheus
Grafana is used to visualise data collected by Prometheus. You can download Grafana from
https://grafana.com/grafana/download
Grafana offers free cloud hosted version with some limitation (1 user, 5 dashboards). Free version is suitable if you are getting started and don’t want to install your own. You can signup for cloud hosted version at
If you decide to install your own Grafana, you can run
cd /usr/local/src wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana_7.3.7_amd64.deb dpkg -i grafana_7.3.7_amd64.deb
Enable and start grafana
systemctl enable grafana-server systemctl start grafana-server systemctl status grafana-server
If you did your own install, grafana runs on port 3000. To access, use url
http://SERVER_IP:3000/login
Default username and passwords are “admin”. Once logged in you will be asked to set password for grafana admin user.
Before you can use Grafana, you need to set a data source and create dash board. In our case, data source is prometheus. To connect Grafana to your Prometheus insallation, go to Settings > Data Sources
On next page, select Prometheus
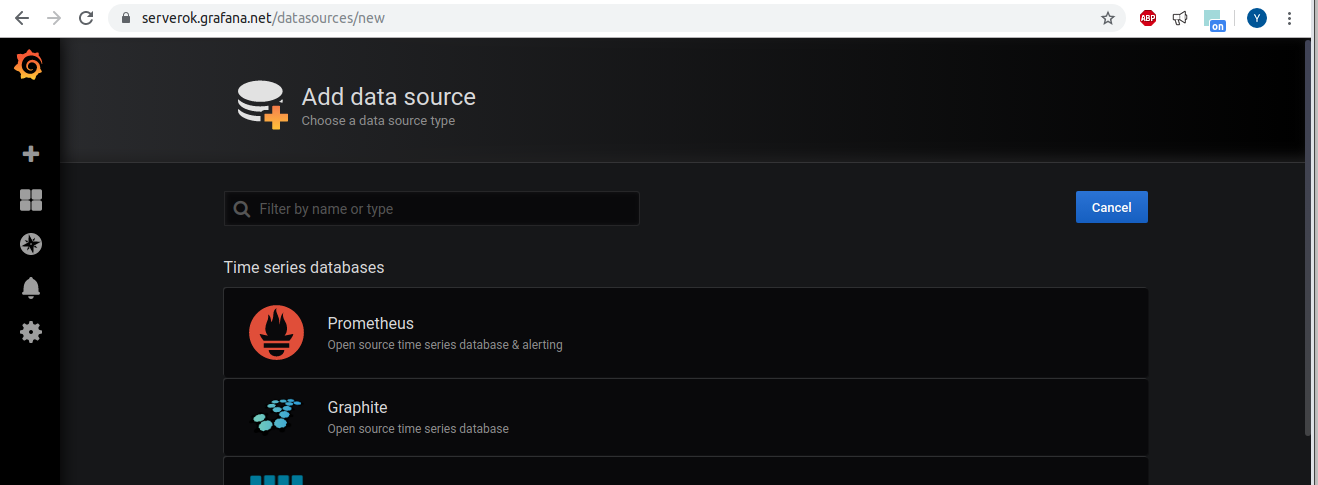
On next page, for URL, enter http://PROMETHUS_SERVER_IP:9090, scroll down, click on “Save & Test” button. If grafana can connect to your prometheus installation, you should see success message with “Data source is working”. If not, you need to check your firewall rules.
Grafana displays data in dash boards. You can create your own or use pre existing dash boards. You can find pre-made dash boards at
https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards
On my grafana installation, i used dashboard
https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/11074
To add this dash board to your Grafana, click on the + button, then select Import. On next screen, you can enter ID for the dash board you need to import. In this case 11074. Click “Load” button to import the dash board.
Here is a dash board for one of the server
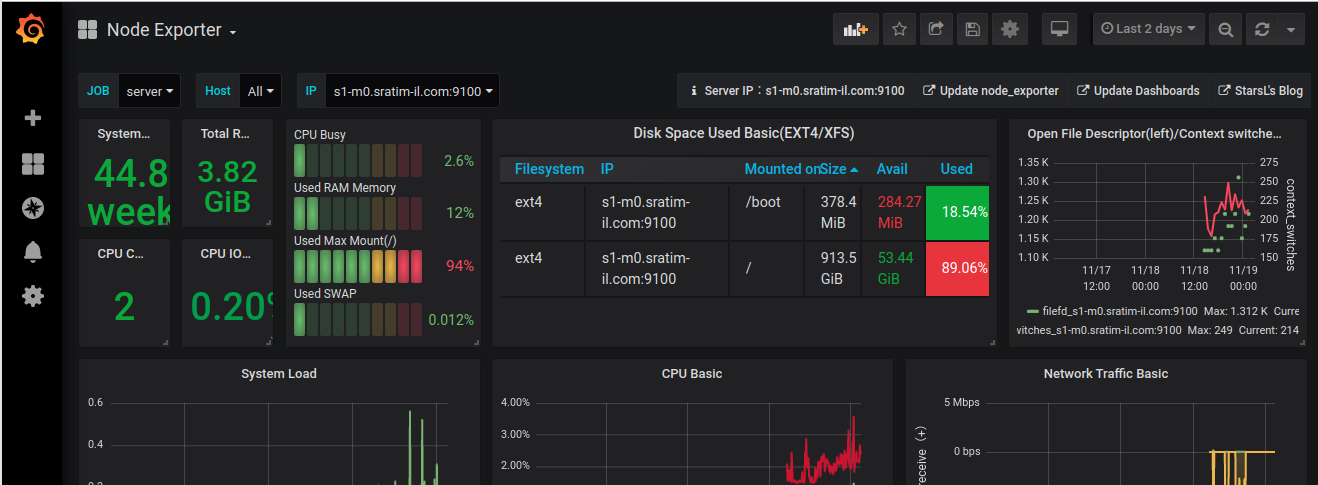
You can edit Panels in grafana dash board to see how it is created. You can create a new dash board with panel you need. This way your dashboards only show required information.
Related Posts
Prometheus Node Exporter on non default port
Prometheus init script for CentOS 6
I moved a web site to new dedicated server. But for some reason, php-fpm crashed. I increased the max_children settings, but it happend again. I do not want down time while i am investigating the problem. So i created a PHP script, that will check if site is working or not.
Script have 2 part.
health-check.php
It is simple PHP script, that get a param and print it.
This file is placed on root of your web site, so it can be accessed using URL http://yoursite/health-check.php
monitor-server.php
Create
mkdir /usr/serverok/ vi /usr/serverok/monitor-server.phpAdd following content
On the script, replace YOUR_DOMAIN_HERE with your actual domain name.
systemctl restart apache2 is for restart apache web server. If you use nginx, replace it. systemctl restart php7.2-fpm restart php-fpm, if you have differnt version of php, you need to change it.
The script is generate a random number, pass it to health-check.php script. Compared the value returned with generated random number to make sure the value is correct. If web server or php-fpm fail, this check will fail.
Now set a cronjob
crontab -eAdd
*/5 * * * * /usr/bin/php /usr/serverok/monitor-server.phpRelated Posts
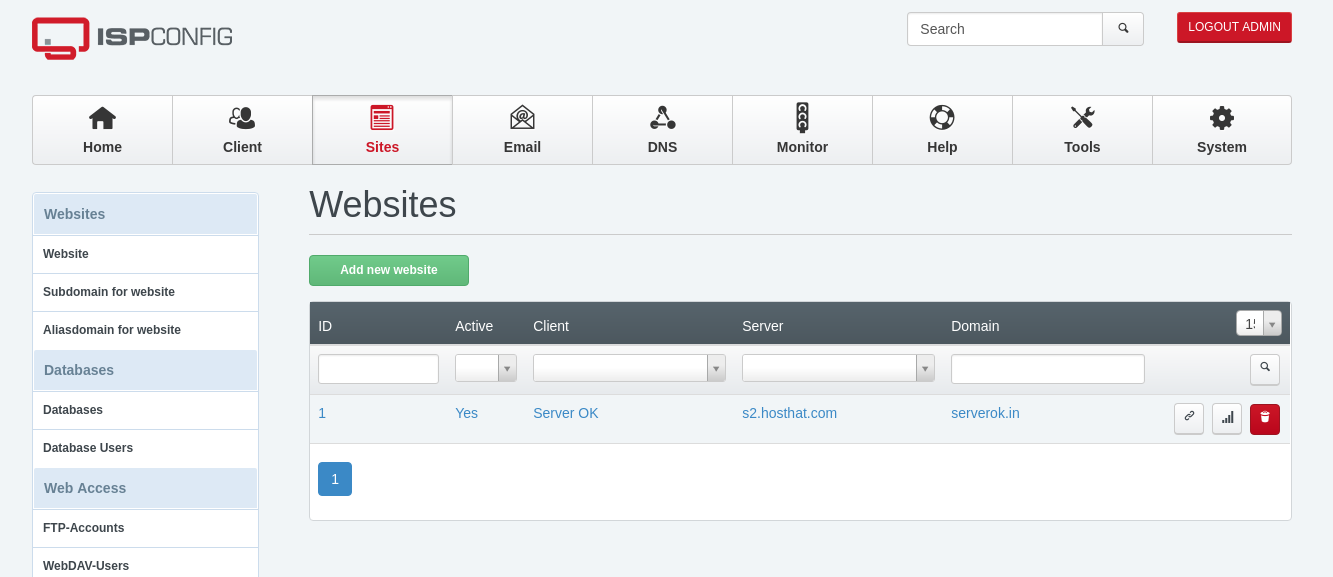
To add SSL for ISPConfig control panel, add the server hostname as a website in ISPConfig and enable the LetsEnrypt checkbox. You can find the server hostname with the command
hostname -f
That will get SSL installed for your hostname. You need to point the server hostname to the server’s IP address to get SSL certificate. Visit server hostname subdomain in a browser and verify SSL works.
Once you have a valid LetsEncrypt SSL certificate installed on your site, create a file
mkdir /usr/serverok/ vi /usr/serverok/ssl-hostname-renew
Add the following content to the file
#!/bin/bash
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/$(hostname -f)/fullchain.pem > /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.crt
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/$(hostname -f)/privkey.pem > /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.key
cat /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.{key,crt} > /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.pem
chmod 600 /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.pem
systemctl restart apache2
cat /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.crt > /etc/postfix/smtpd.cert
cat /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.key > /etc/postfix/smtpd.key
service postfix restart
service dovecot restart
cat /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl/ispserver.pem > /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
chmod 600 /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
service pure-ftpd-mysql restart
If you use nginx webserver, replace apache2 with nginx.
Make the script executable
chmod 755 /usr/serverok/ssl-hostname-renew
Run the script to activate SSL for the ISPConfig control panel, FTP, and mail server.
/usr/serverok/ssl-hostname-renew
Now set a cronjob
crontab -e
Add
@weekly /usr/serverok/ssl-hostname-renew > /dev/null
Now you should be able to access ISPConfig with a valid SSL certificate on URL
https://HOSTNAME:8080
Back to ISPconfig

apachectl command is used to interact with Apache web server.
To see Apache status
apachectl status
To list virtualhost info, run
apachectl -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS
List VirtualHost + server config.
apachectl -S
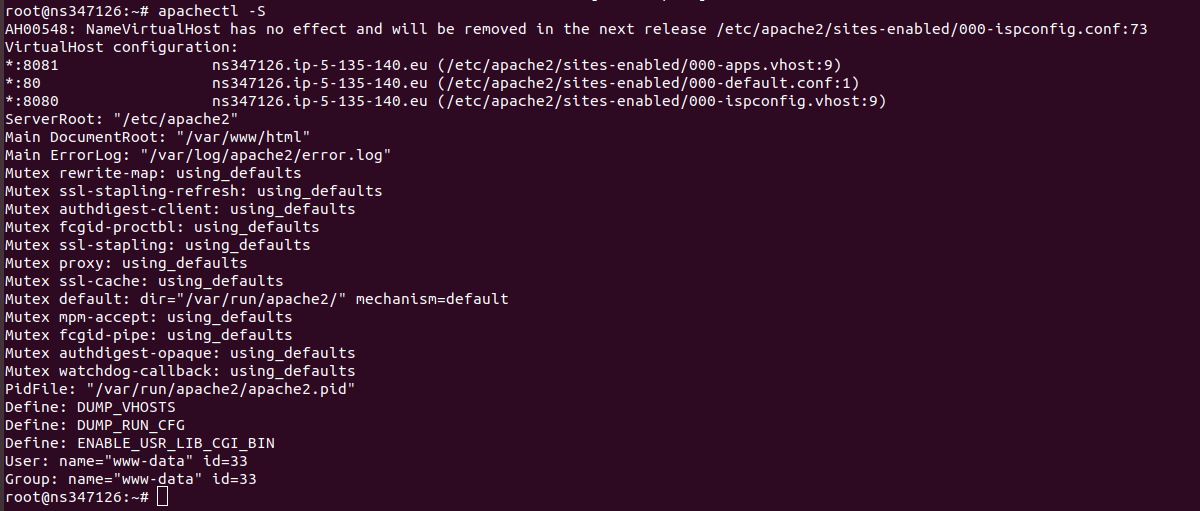
To list loaded apache modules, run
apachectl -M
Related Posts
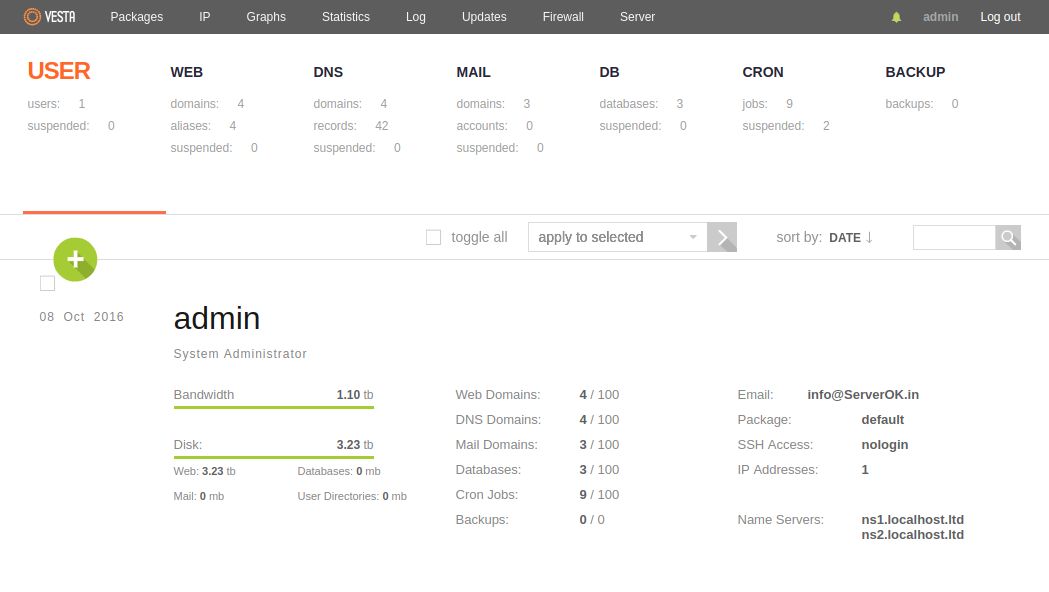
VestaCP install self signed SSL for mail server by default. To install valid SSL, login to VestCP, go to sites. You will see a site with your sites hostname. If you don’t see it, create a site with your server hostname. Make sure DNS edited so hostname resolve to server IP. Now you should be able to get free LetsEncrypt SSL for this site.
if you check Apache Virtual Host for the site, you will see someting like
SSLCertificateFile /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.HOSTNAME.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.HOSTNAME.key SSLCertificateChainFile /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.HOSTNAME.ca
In VeataCP the config files for exim and dovecot located at
/etc/exim4/exim4.conf.template /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf
These configs use SSL located at /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.crt and /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.key.
To use the FREE SSL, create a bash script.
mkdir /usr/serverok/ vi /usr/serverok/ssl-renew-hostname
Add
#!/bin/bash # Author: ServerOk Software # Web: www.serverok.in # Email: admin@serverok.in cat /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.HOSTNAME.crt > /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.crt cat /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.HOSTNAME.ca >> /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.crt cat /home/admin/conf/web/ssl.HOSTNAME.key > /usr/local/vesta/ssl/certificate.key systemctl restart apache2 systemctl restart exim4 systemctl restart dovecot /usr/local/vesta/nginx/sbin/vesta-nginx -s reload
make the file executable
chmod 755 /usr/serverok/ssl-renew-hostname
Run the script
/usr/serverok/ssl-renew-hostname
Now SSL will work for mail server and VestaCP. To access VestaCP, use
https://HOSTNAME:8083/login/
You can view mail server SSL with command
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect HOSTNAME:993 openssl s_client -showcerts -connect HOSTNAME:465 openssl s_client -starttls smtp -showcerts -connect HOSTNAME:587
Replace HOSTNAME with actual hostname of your server.
LetsEncrypt SSL expire every 90 days. So we will create a cronjob to auto renew SSL. Ff you have a paid SSL, you don’t need this cronjob
Create a cronjob with
crontab -e
Add
@weekly /usr/serverok/ssl-renew-hostname > /dev/null 2>&1
Related Posts