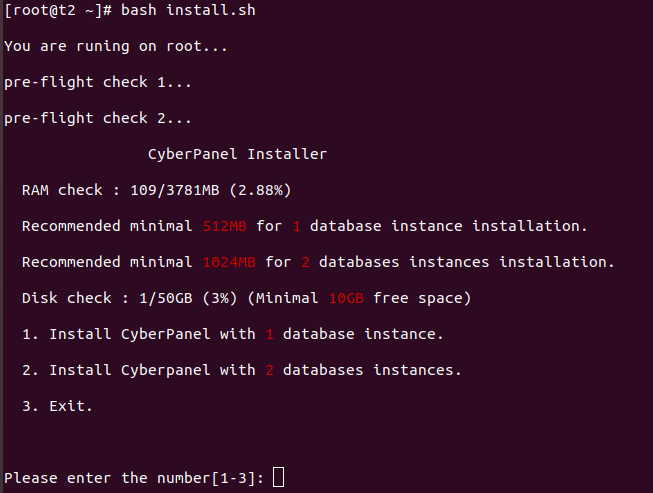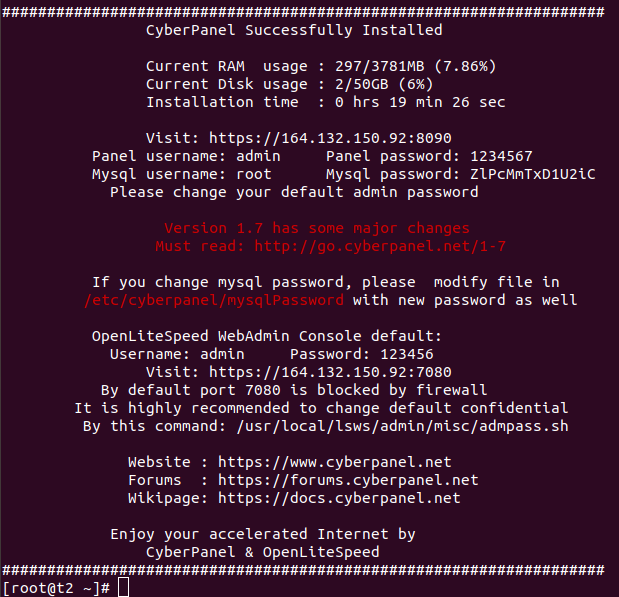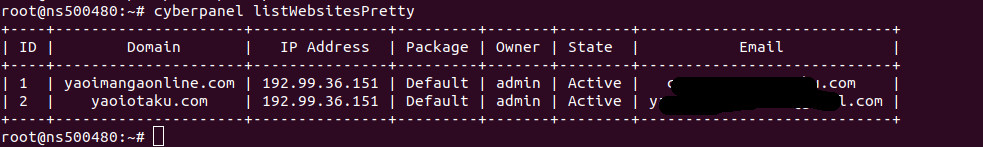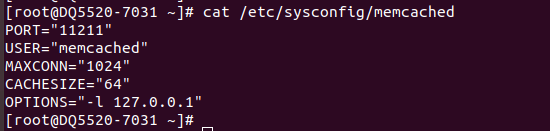
Webmin run on port 10000 over HTTPS. By default webmin use self signed SSL certificate. To use SSL for webmin, you need to first get SSL cerificate for the domain you need to use. Refer https://serverok.in/letsencrypt for getting SSL certificate.
Once you have SSL certficate, do following.
cd /etc/webmin mv miniserv.pem miniserv.pem.old cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOURDOMAIN/cert.pem /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOURDOMAIN/privkey.pem /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOURDOMAIN/chain.pem > /etc/webmin/miniserv.pem
Now restart webmin
systemctl restart webmin
Now you will be able to access webmin using this SSL cert at
https://YOURDOMIN:10000
To auto renew SSL, add following entry to cronjob that renew your LetsEncrypt SSL certificate.
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOURDOMAIN/cert.pem /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOURDOMAIN/privkey.pem /etc/letsencrypt/live/YOURDOMAIN/chain.pem > /etc/webmin/miniserv.pem systemctl restart webmin